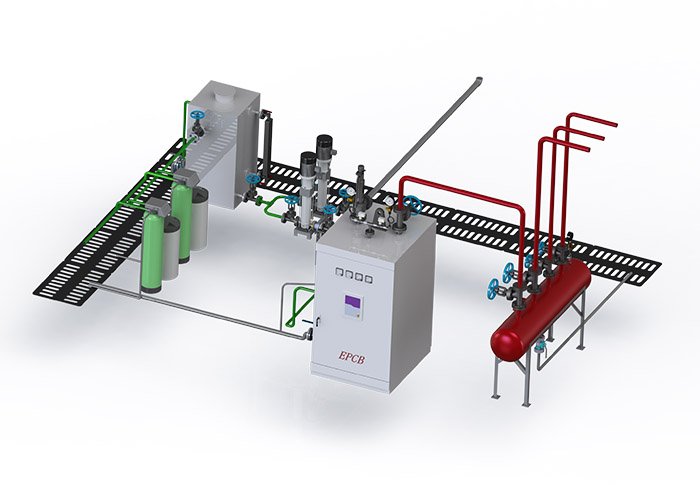
Under the background of the continuous growth of global energy demand, how to realize the sustainability of energy supply has become a major challenge for all countries. Traditional fossil fuels are gradually being replaced by environmentally friendly energy because of their non-renewable and high carbon emission characteristics. Renewable energy, with its clean, efficient and sustainable advantages, plays a vital role in the global energy structure transformation.
As an important part of renewable energy, biomass energy has unique advantages. It takes organic waste as raw material, and through the recycling of natural resources, it not only realizes carbon neutrality, but also effectively reduces the pressure of waste on the environment, Compared with renewable energy sources such as wind energy and solar energy, biomass energy has the characteristics of wide sources of raw materials, convenient storage and transportation, flexible application, etc., and is especially suitable for energy demand in industrial production and agricultural areas.Under the global common goal of reducing carbon emissions and improving energy security, biomass energy is increasingly supported by policies and concerned by the market, and has become an important force to promote the energy revolution.
Overview of Biomass Energy

The definition of biomass
Biomass energy refers to a form of energy that produces renewable fuel by usingorganic wastes of animals and plants. lts core feature is carbon neutrality, that is, theamount of carbon dioxide released in the process of biomass combustion is basically
the same as that absorbed by raw materials through photosynthesis during theirgrowth, Therefore, biomass energy can not only provide stable support for the energysystem, but also significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, which is of greatsignificance for mitigating climate change.
Learn More:The advantages of using biomass in boilers
Access to biomass
Biomass energy sources are extensive, mainly including the following ways:
Agricultural wastes:Straw, rice husk, peel of crops and waste from orchard pruning are all important raw materials for biomass energy. This kind of waste has a stable source and is especially suitable for energy development in large agricultural countries.
Forestry residues:Bark, sawdust produced in the process of logging and pruning waste in forest management are high-quality woody biomass fuel sources. This kind of material can not only reduce the accumulation of forest waste, but also improve the utilization rate of resources.
Animal husbandry waste:After proper treatment, livestock manure can be used as biogas or dry fuel. This method can not only effectively treat animal husbandry waste, but also provide clean energy for rural areas.
Human waste:Organic waste (such as kitchen waste) and yard pruning waste in municipal waste can also be used for power generation or heating through biomass conversion technology. The development of such resources can not only reduce the pressure on landfills, but also provide green energy solutions for cities.
Utilization Mode of Biomass Energy
Biomass energy forms
Biomass energy can be transformed into energy forms needed in our daily life and industrial production in many ways, mainly including the following three:
heat energy:Biomass directly releases heat energy through combustion for heating or hot water production. Its combustion efficiency is high, and it is especially suitable for heating systems of homes and commercial buildings, as well as thermal energy supply of industrial boilers.
electric energy:Biomass drives steam turbines or internal combustion engines to generate electricity through gasification or combustion, providing clean electricity for industry, commerce and families. Biomass power generation technology has been widely used in many countries.
Fuel:Biomass can be processed into various fuel forms, including solid fuel (such as sawdust particles and compressed straw), liquid fuel (such as biodiesel and bioethanol) and gas fuel (such as biogas). These fuels can be widely used in transportation, industrial production and residents' lives, providing an important alternative to reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Application scale
The application of biomass energy is flexible and diverse, which is not only suitable for small-scale local use, but also meets the needs of large-scale industry:
Small-scale application:Household boiler: Many families use biomass boilers or fireplaces, using sawdust particles or compressed straw as fuel to provide heating and hot water for houses. This method is economical and efficient, especially suitable for rural areas or areas rich in forest resources.
Building heating: Small and medium-sized buildings, such as schools, hospitals and commercial places, often use biomass heating systems to heat buildings through centralized combustion, reducing dependence on traditional fossil fuels.
Large-scale application:Biofuel factories: By converting agricultural wastes, forestry residues and municipal refuse into liquid fuels or gas fuels, these factories provide a large number of renewable fuels for transportation and industry, which helps to alleviate the energy shortage problem.
Industrial boilers: In large-scale industrial production, biomass boilers are widely used to provide heat energy to support the production needs of high-energy industries such as food processing, textile and paper making. Industrial-grade biomass boiler has higher combustion efficiency and greater heat output capacity, which is a green alternative to fossil fuel boiler.
Types of Biomass Fuel

Wood fuel
Wood fuel is one of the most common types of biomass energy, which has various sources and is widely used in the fields of heating, power generation and fuel production.
Forest residues
In the process of logging and forest management, a large number of wood fragments, including branches, bark and sawdust, are usually produced. After collection and processing, these materials can be used as efficient wood fuel sources, effectively improve the utilization rate of forest resources and reduce the impact of waste accumulation on the environment.
Factory residues
Wood processing plants and furniture manufacturing plants will produce a large number of by-products, such as sawdust, sawdust and scraps. These by-products can be converted into fuel particles by compression molding technology, which are widely used in domestic boilers and industrial heating systems.
Agricultural residues
Agricultural wastes such as crop straws, branches from orchard pruning and rice husk can also be converted into wood fuel. This method not only reduces the incineration pollution of agricultural waste, but also provides an economical and efficient energy choice for rural areas.
Urban wood and yard waste
Urban garbage contains a lot of woody organic matter, including yard pruning waste, construction waste wood and so on. After classification and treatment, these wastes can be used as an important supplementary source of biomass fuel, which provides a solution for the resource utilization of municipal waste.
Special biomass crops
Some crops are specially planted for biomass energy projects, such as corn, rapeseed and willow. These crops usually have the characteristics of high biomass yield and rapid growth, which can ensure the stability and sustainability of fuel supply.
Chemical Recovery of Fuel (Black Liquor)
Black liquor is a by-product of extracting cellulose from wood in paper industry, which is rich in lignin and other organic substances. It can be used as biomass fuel for power generation or heating, which not only realizes the resource utilization of waste, but also reduces the environmental pollution of paper industry.
Animal manure
Animal manure is another common source of biomass fuel, especially in rural areas and developed areas of animal husbandry.
Dry animal manure
Dry animal manure with water content below 30% is suitable for composting or direct combustion. Its high calorific value is an economical and practical energy choice, especially in areas lacking other fuel resources.
Wet livestock manure (cow manure slurry)
High-moisture feces from modern dairy farms are usually collected by flushing system. This kind of manure can be used for biogas production, and methane can be generated through anaerobic fermentation, providing clean and renewable gas energy for rural areas.
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW)
Municipal solid waste (MSW) is another important source of biomass fuel, especially in areas with high degree of urbanization.
Residential organic waste
Including kitchen waste, peels and plant residues. These wastes can be converted into biogas or liquid fuel by fermentation or pyrolysis technology, providing green energy support for urban energy system.
Construction wood waste
Waste wood in construction waste, such as waste furniture and decoration waste, can be used as fuel after classification. This not only reduces the burden of landfill, but also provides a stable source of raw materials for biomass energy production.
Supply and cost of biomass fuel

Energy density and transportation cost
Biomass fuel has low energy density, and it needs more fuel to produce the same heat or energy output compared with traditional fossil fuels. For example, biomass fuels such as sawdust particles or straw have lower calorific value per unit weight than coal or oil. This means that in practical applications, the demand for fuel storage and transportation will increase.
In addition, biomass fuel usually contains high moisture, which not only reduces the combustion efficiency, but also significantly increases the transportation cost. The fuel with high moisture content is heavier, and the cost and energy consumption during transportation also increase. Therefore, in the actual utilization of biomass fuel, reducing the water content of fuel is an important measure to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Supply stability and seasonality
The supply of biomass fuel is significantly affected by seasonal factors. For example:
Agricultural wastes: Crop straws, fruit shells and other materials are usually produced after the harvest season, and their supply has strong seasonal fluctuations.
Forest residues: The life cycle of logging and forest management will also affect the availability of fuel.
Animal manure and municipal waste: These fuels are relatively stable, but they may still be affected by weather or regional factors.
In order to cope with supply fluctuations, biomass energy projects need to have the ability to adjust production plans or store large quantities of fuel. For example, fuel is stored when the supply is sufficient and gradually consumed in the off-season to ensure the stability of continuous operation.
Cost control strategy
In the economic utilization of biomass fuel, transportation cost is one of the key factors affecting the overall economic benefits. The following strategies can effectively reduce costs:
On-site consumption: try to use biomass fuel near the fuel source to reduce transportation links. For example, farms or forest farms can directly use local waste to provide fuel for boilers or biogas equipment.
Short-distance transportation: If it is impractical to use on site, try to control the transportation distance of fuel within 50 miles to avoid the high cost caused by long-distance transportation.
Optimize fuel treatment: By drying and compressing the fuel, the energy density per unit weight can be increased, thus reducing transportation costs and storage space requirements.
Biomass Industrial Boiler
Biomass boilers use biomass fuels such as sawdust, straw, rice husk and wood particles as energy sources, and generate heat energy through combustion for steam, hot water or hot oil supply. Its workflow includes fuel supply, combustion, heat transfer, flue gas treatment and thermal energy output. Fuel enters the combustion chamber by means of screw transportation and chain transportation, and undergoes three stages of drying, pyrolysis and combustion, releasing heat. The high-temperature flue gas undergoes heat transfer from the hot surface, which raises the temperature of boiler water or heat transfer oil. Flue gas emissions need to be treated by purification equipment such as cloth bags and electrostatic precipitators, and some boilers are equipped with desulfurization and denitrification devices to reduce pollutant emissions. According to the demand, biomass boilers can provide steam (suitable for food, chemical industry, textile and other industries), hot water (heating, medical treatment, pharmacy) or heat transfer oil (chemical industry, wood processing, food drying) and other forms of heat energy.

Biomass boiler is widely used in many industries because of its advantages of energy saving and environmental protection. Textile printing and dyeing industry uses its stable steam for fabric treatment to improve energy efficiency and reduce carbon emissions; The food processing industry relies on its clean heat source for drying, sterilization and cooking; The chemical industry uses biomass heat transfer oil boilers to provide high-temperature heat energy above 300℃ to ensure safety and efficiency; Paper industry can use it to meet steam demand and recycle waste wood to reduce costs; The building materials industry relies on its thermal energy to support the production of cement, glass and bricks and improve efficiency; The pharmaceutical industry provides clean steam through biomass boilers, which meets GMP standards; In the fields of aquaculture and agricultural processing, it is used for heating, feed drying and agricultural products processing, and agricultural waste is fully used as fuel to reduce production costs.
Biomass boiler has obvious advantages of energy saving and environmental protection. Replacing traditional fossil fuel with renewable biomass fuel can effectively reduce carbon emissions. At the same time, the price of biomass fuel is low, and some industries can also use their own waste as fuel, further reducing operating costs. In addition, the boiler adopts advanced combustion technology and flue gas recovery system, so that the thermal efficiency can reach more than 85%. Its low emission characteristics ensure compliance with global environmental protection policies and help enterprises avoid production stagnation or fines caused by environmental failure.
Learn More:The Ultimate Guide to Biomass Boilers
Advantages of Biomass Energy
With the adjustment of global energy structure and the development of renewable energy technology, biomass energy has become a green energy choice of great concern because of its advantages of sustainability, circular economy value, employment promotion and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.

Sustainability and economy
Biomass energy comes from a wide range of sources, including agricultural waste (such as straw, rice husk and fruit shell), forestry waste (such as sawdust and sawdust), urban organic waste and industrial by-products. These renewable resources can be supplied sustainably through scientific management and rational development, thus avoiding the non-renewable problem of fossil fuel resources. In addition, the development of biomass energy promotes the utilization of agricultural and forestry wastes, reduces the environmental pollution caused by incineration or landfill, reduces the cost of waste treatment and improves the utilization rate of resources. In terms of energy supply stability, biomass fuel production can be adjusted according to market demand. Compared with energy sources such as oil and natural gas, it is less affected by fluctuations in the international energy market, which improves energy security.
Circular economy
Biomass energy conforms to the concept of circular economy, and realizes efficient recycling of resources by converting agricultural, forestry and industrial wastes into energy. For example, crop straws, wood processing residues and livestock manure can be used to produce biomass pellet fuel or biogas, thus reducing the environmental pollution caused by wastes. In addition, the ashes from biomass boilers are rich in minerals such as potassium and phosphorus, which can be used as agricultural fertilizers to promote soil fertility and reduce the use of chemical fertilizers, thus reducing the impact of agricultural production on the environment. Compared with traditional fossil fuels, biomass energy has lower carbon emissions when burning, which can effectively reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve energy efficiency and achieve sustainable economic development.
Promote employment
Biomass energy industry covers fuel collection, processing, transportation, boiler manufacturing and maintenance, which can create a large number of employment opportunities, especially in areas rich in agricultural and forestry resources. For example, biomass fuel processing plants, boiler manufacturing enterprises and biogas power generation projects all need a lot of manpower support to provide long-term and stable jobs for the local area. For economies that rely on fossil fuels, the development of biomass energy can provide re-employment opportunities for workers who are unemployed due to energy structure adjustment, and help achieve social stability in the process of energy transformation. In addition, in developing countries, biomass energy projects can also provide clean energy for rural and remote areas, reduce energy poverty and improve the quality of life of residents.
Reduce dependence on fossil fuels
Under the background of global promotion of carbon neutrality, biomass energy can provide effective alternatives in areas that are difficult to decarbonize, such as heavy transportation, aviation and industry. For example, biomass liquid fuels (such as biodiesel and ethanol fuel) can partially replace petroleum fuels and be used in trucks, ships and airplanes to reduce carbon emissions. In addition, biomass energy can be used for high-temperature industrial heating, such as steel, cement and chemical industries, providing renewable energy options for these traditional high-energy-consuming industries and reducing dependence on coal and natural gas. With the development of biomass energy technology, countries can reduce their dependence on imported fossil fuels in the process of energy structure adjustment, enhance energy autonomy and improve energy security.
Conclusion
As a renewable and low-carbon clean energy, biomass energy plays an important role in promoting sustainable development and reducing carbon emissions. Its extensive resource base, circular economy value, employment promotion effect and substitution potential in difficult decarbonization fields make it an important choice for global energy transformation. Especially in the industrial field, biomass boilers are helping various industries to move towards green production because of their advantages of high efficiency, environmental protection and economy. As a leading boiler manufacturer in the industry, EPCB boiler provides enterprises with efficient and low-emission biomass boiler solutions by virtue of advanced combustion technology, efficient heat energy conversion and intelligent control system, ensuring more energy-saving and environmental protection in the production process. With the continuous innovation of technology and the promotion of global policies, EPCB boilers will continue to help enterprises optimize energy utilization, improve production efficiency and jointly promote a green and low-carbon future.
 Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler