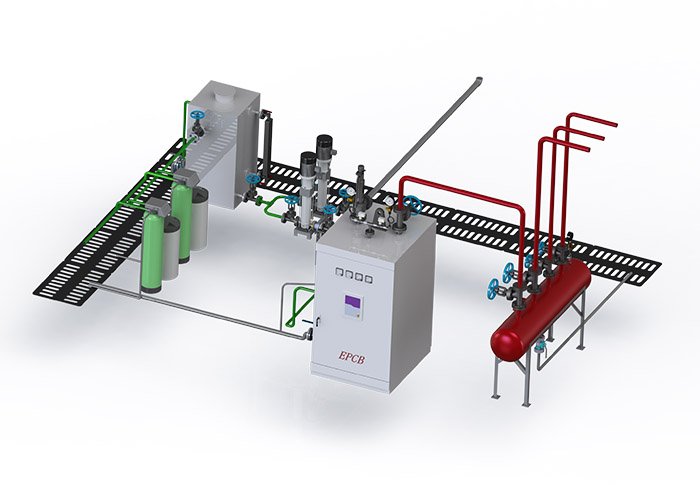
Introduction to Biomass Briquette Fuel
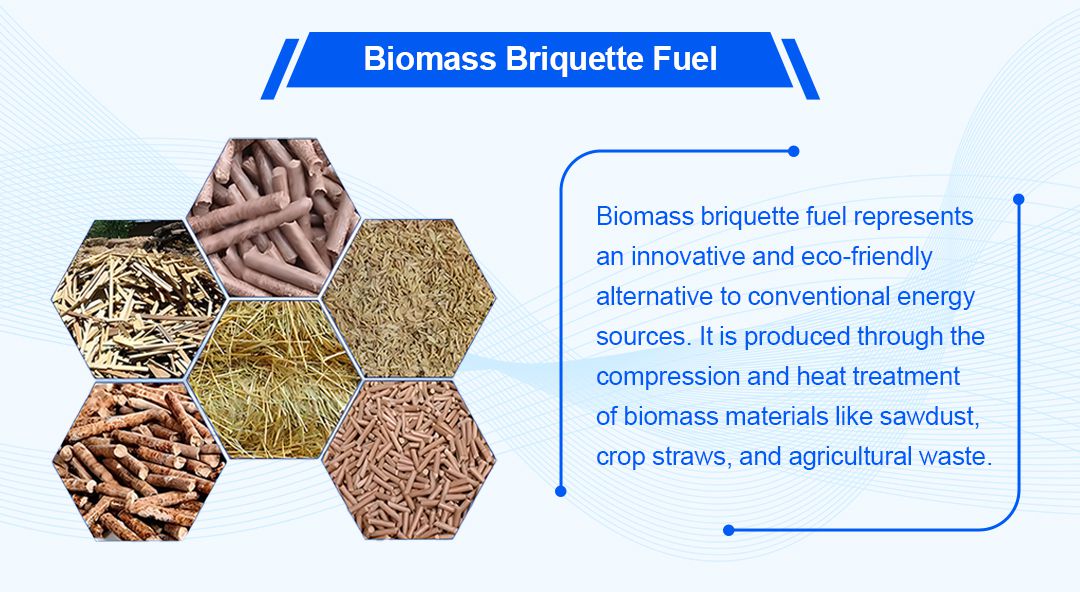
Biomass briquette fuel is eco-friendly. It is an alternative to traditional fuels. It is an emerging energy source. It is made from biomass materials, like wood chips, straw, and waste crops. They are compressed and heated. This usually forms them into pellets or blocks. They are highly efficient, non-toxic, and renewable.
The global pollution problem is growing. Many countries have turned to biomass fuels to fight air and greenhouse gas pollution. It is carbon-neutral. This is because it releases as much carbon dioxide as it absorbs.
Also, biomass briquette fuels are a renewable energy source. They do not run out. They reduce reliance on fossil fuels and help drive an energy transition. They boost sustainable development. They will be a key energy sector direction in the future.
The Role of Biomass Briquette Fuels in Global Energy Consumption
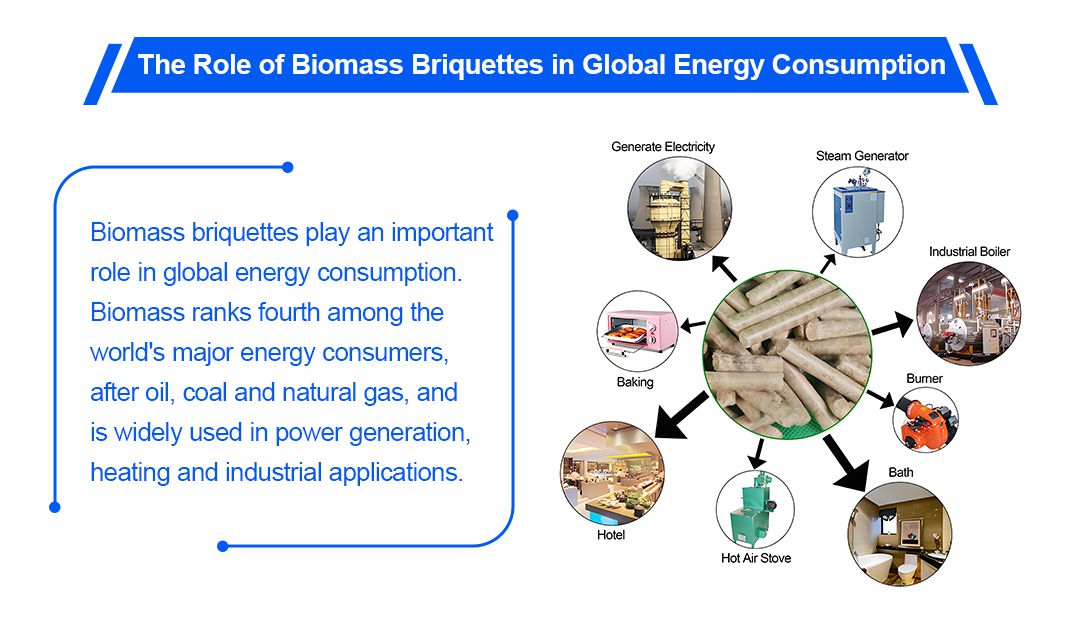
Biomass briquette fuels play an important role in global energy consumption. The International Energy Agency (IEA) says biomass ranks fourth. It comes after oil, coal, and natural gas among the world's major energy consumers. Biomass is gaining ground as a renewable energy source. It is widely used for power, heating, and industry.
As a result, the role of biomass briquette fuels in global energy consumption is gradually increasing. Biomass has a small share of energy use. But, its importance is growing. This is as demand for renewable energy rises. Especially in some developing countries and rural areas, biomass moulded fuels are one of the main sources of energy for heating, cooking and other daily life uses.
In addition, biomass forming fuels have shown many advantages in boiler use. The use of biomass forming fuels in boilers has some obvious advantages over coal. Biomass forming fuel produces less particulate matter and other harmful substances when it burns. This reduces air pollution. Also, they are easier to get and store. They come from fertiliser sources like agricultural waste and wood waste. Again, burning biomass to make fuel is more efficient. It can provide a relatively stable heat output. In addition, biofuels are cheap and easy to get. They are widely used in some regions for heating and industry, among other uses.
Characteristics of Biomass Briquette Fuel
Biomass briquettes are solid fuels made from renewable biomass materials that offer many advantages that make them an important alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
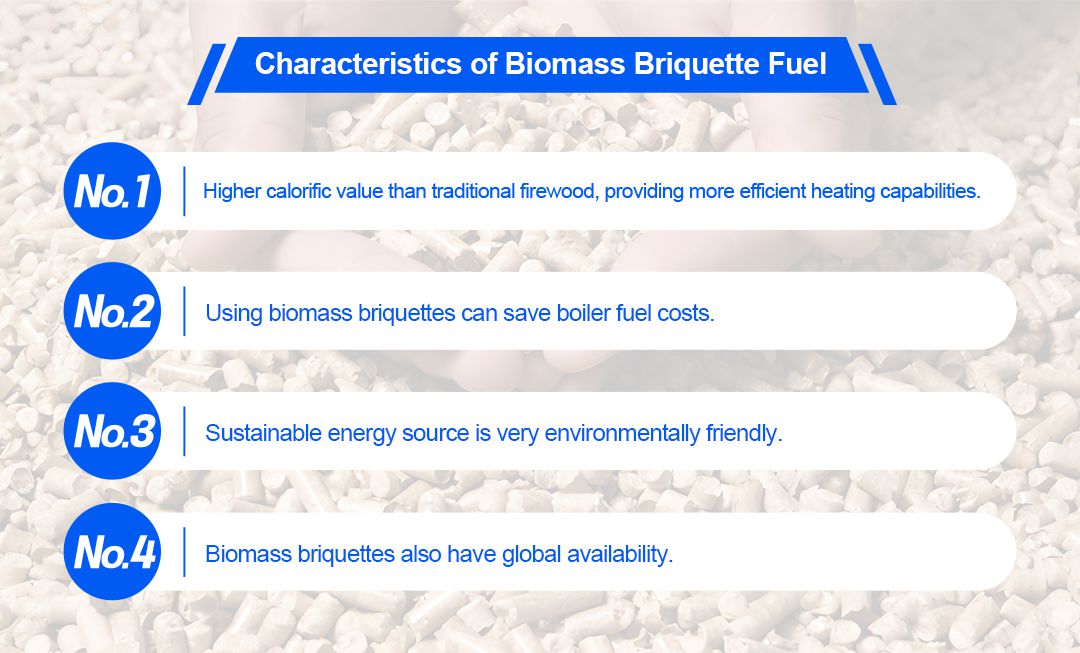
First, it has a higher calorific value than traditional firewood, providing more efficient heating capabilities. This means that under the same combustion conditions, biomass briquette fuel can provide users with more heat energy, improving its application efficiency in the industrial field.
Secondly, the use of biomass briquette fuel can save boiler fuel costs, because biomass resources are relatively abundant and can be produced from crop residues, wood waste and other raw materials, which reduces production costs and reduces dependence on imported fuels, which is conducive to improving Energy security.
Additionally, this sustainable energy source is very environmentally friendly. Compared with using coal as the main energy source, less greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides are emitted during the production process, and the negative impact on the environment is smaller. In addition, the production and utilization process of biomass briquette fuel is relatively clean, reducing pollution to water resources and soil.
In addition to the above advantages, biomass briquettes also have global availability. Since vast amounts of potentially renewable resources exist around the world, this type of sustainable energy can help reduce the need for restrictive resources such as natural gas and oil and boost economic development. The renewable nature of biomass briquette fuel gives it a longer-term sustainable development prospect.
Types of Biomass Boilers
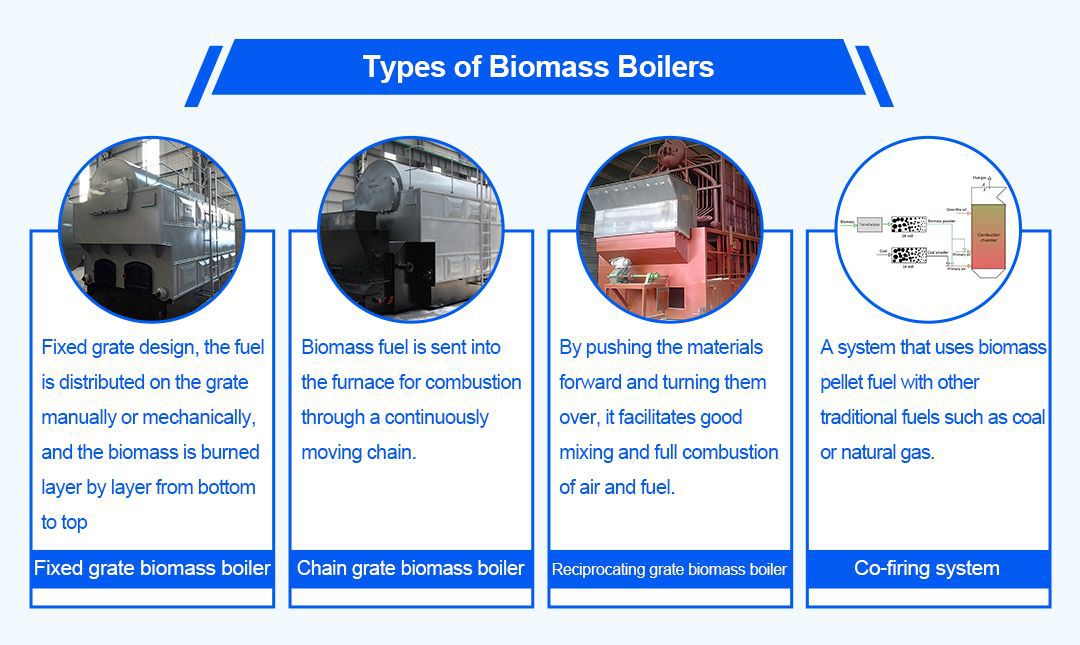
Biomass boilers can be split into various types by their combustion methods and grate structures. EPCB Boiler's biomass boiler product line has three types: fixed grate, chain grate, and reciprocating grate boilers.
Fixed grate biomass boilers: These boilers are designed with a fixed grate, where the fuel is distributed evenly on the grate manually or mechanically, and the biomass is burned layer by layer from the bottom up as the grate temperature rises. This type of boiler is suitable for burning poorly formed or short biomass fuel.
Chain grate biomass boiler: chain grate is a more common form of biomass boiler, through the continuous movement of the chain will be biomass fuel into the furnace chamber for combustion. Chain grate is suitable for burning all kinds of well-formed biomass fuels, such as biomass pellets, stick fuels, etc., with a good degree of automation and high combustion efficiency.
Reciprocating grate biomass boiler: the grate piece of this kind of boiler will do reciprocating movement, by pushing the material forward and turning the material, in order to facilitate the good mixing of air and fuel and full combustion. Reciprocating grates are also suitable for moulded biomass fuels within a certain particle size range and help to improve combustion efficiency and reduce incomplete combustion products.
Also, there are co-firing systems. They use biomass moulding fuels with coal or natural gas. These systems are typically used in existing coal-fired boilers to co-fire biomass fuels by adjusting the fuel ratio. Co-firing systems have an advantage. They let us use biofuels to cut fuel costs and reliance on fossil fuels. And, we can do this without changing existing equipment. Also, co-firing systems can achieve higher combustion rates. This is because biomass-derived fuels can burn more efficiently with the coal ash during co-firing.
Co-firing is a technology that mixes biomass fuels with fossil fuels (e.g. coal) in the same boiler for burning together. It is one of the cheapest methods. It has the following features:
Optimisation of resource utilisation: it can effectively utilise existing coal-fired boiler facilities and reduce investment in new dedicated biomass boilers.
Emission reduction advantage: biomass fuels have relatively low carbon emissions, and partial replacement of coal combustion can reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Economy: The cost of biomass fuel is usually lower than that of fossil fuels, especially with the support of subsidy policies, and the use of excess agricultural waste or forestry residues as fuel can reduce costs, while also solving the problem of disposal of these wastes.
Combustion rate enhancement: A reasonable mix of biomass and fossil fuel ratios can improve combustion characteristics, increase combustion efficiency and reduce pollutant emissions, especially when equipped with advanced combustion technologies and flue gas cleaning devices.
Impacts on Gaseous Pollutants and Air Quality
Burning biomass fuels significantly increases the emission of gaseous pollutants. These pollutants harm air quality and directly cause health problems like respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer.
Statistics show that biomass molding fuels could help ensure energy security and cut greenhouse gas emissions. But, in practice, biomass fuels also make some carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and other pollutants.
Carbon dioxide (CO2): Burning biomass fuels releases carbon dioxide. But, it is reabsorbed from and by the atmosphere during plant growth. In the long term, the net impact of biomass moulding fuel use on global greenhouse gas emissions is relatively low.
Nitrogen oxides (NOx): NOx are harmful to the atmosphere. They can cause problems like acid rain and ozone pollution. But, biomass-formed fuels usually emit less NOx than coal and oil.
It is worth noting that biomass molding fuels may cause some extra pollution. But, they are still much better than traditional energy sources. We are a professional boiler manufacturer. We respond to environmental policies and are committed to making products that save energy and resources. These products benefit our customers and society. We have adopted many improvement strategies. These include using high-efficiency combustion equipment, doing regular maintenance and cleaning, and avoiding incomplete combustion. The goal is to minimize pollutant emissions to protect the environment and human health.
Biomass Briquette Fuels in Developing Countries
In developing countries, especially those with large populations like India and China, biomass briquette fuels play an important role in rural heating and cooking. Rural areas in these countries often rely on traditional biomass fuels such as firewood and charcoal to meet household energy needs. However, the use of such traditional fuels leads to many negative impacts such as air pollution, deforestation, and health problems. Therefore, switching to biomass briquette fuels as fuels is a sustainable solution that is important for improving the environment in which people live and reducing their dependence on natural resources.
In countries such as India and China, various initiatives have been taken by governments and NGOs to promote the use of biomass briquette fuels, particularly biomass briquettes as an alternative to boiler fuel:
Governments and various organizations have begun to support the production and supply of biomass briquette fuels to replace traditional charcoal. Biomass molded fuels are usually made from compressed and processed biomass waste, straw, wood chips, and other feedstocks, a form of energy that can help rural dwellers save money and improve their standard of living due to its renewable nature and cheaper price.
The government and relevant organizations are also actively promoting the use of biomass molding fuel as boiler fuel. They do so by retrofitting existing coal-fired boilers or promoting new types of biomass boilers that can burn biomass briquette fuel more efficiently and reduce the need for traditional fuels, thereby reducing environmental pollution and health risks.
The Government and NGOs have also been actively engaged in publicity and education activities to disseminate knowledge and technology of biomass-forming fuels to rural residents, and to raise their awareness of environmentally friendly energy and its use. This takes the form of providing training, demonstration programs, pamphlets, etc. to help rural residents understand the advantages of biomass briquette fuels and how to use them.
With continued technological advances and increased government support, we could see biomass briquette fuels achieve wider and more sustainable applications in developing countries.
Challenges and Criticisms of Biomass Briquette Fuels
Although considered environmentally friendly and sustainable as a renewable energy source, biomass briquette fuels face several challenges and criticisms.
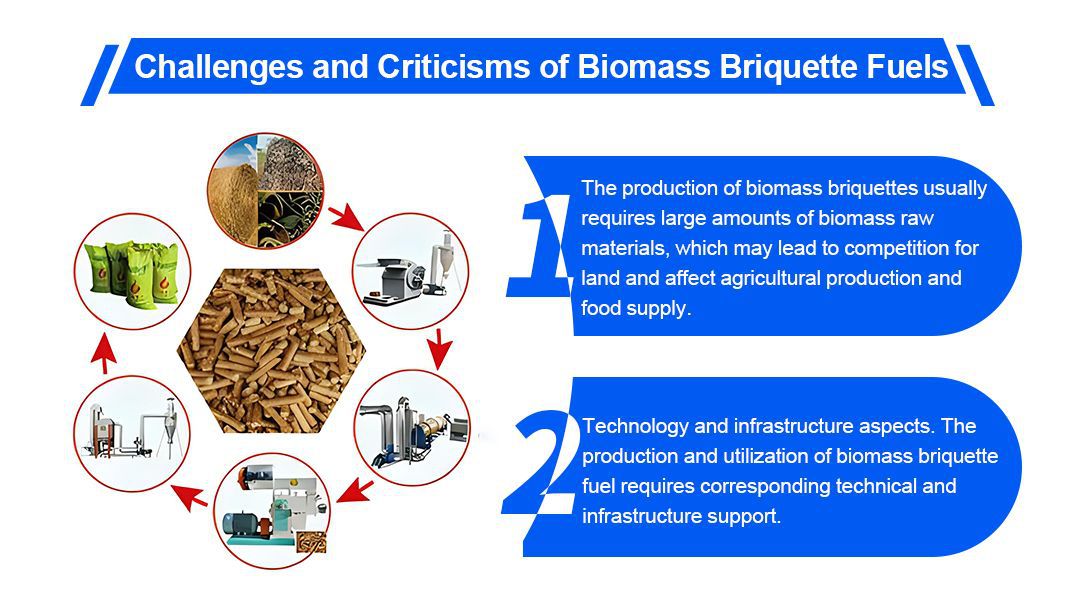
Firstly, the production of biomass-derived molded fuels usually requires large amounts of biomass feedstock, which may lead to competition for land, affecting agricultural production and food supply. In some areas, the cultivation of large quantities of energy crops for the production of biomass-derived molded fuels may lead to land diversion and deforestation, which in turn affects the ecological balance and food security. Therefore, a balance needs to be found between biomass production and food production to ensure that biomass production does not negatively affect agriculture and food supply.
Another challenge is in terms of technology and infrastructure. The production and utilization of biomass for forming fuels require appropriate technological and infrastructural support, including biomass collection, processing, conversion, and transport. In some developing countries, these technologies and infrastructures may be underdeveloped, limiting the widespread use of biomass-derived fuels. In addition, there are some technical difficulties in the production and utilization of biomass-forming fuels, such as inefficient biomass treatment and conversion, and poorly adapted combustion equipment, which require further research and improvement.
All in all, despite the above challenges and other criticisms, we can still see that more and more countries are beginning to pay attention and invest in advancing the development of biomass-forming fuel technology. In the future, with technological advances and measures to address land use issues, we believe that biomass fuels will play an increasingly important role and contribute to reducing dependence on limited resources and protecting the environment.
Conclusion
Biomass briquette fuel has significant potential as a sustainable energy source. It can reduce carbon emissions, improve air quality and increase energy security. However, issues such as land use conflicts, technical and infrastructural challenges, and socio-economic impacts need to be overcome. Future progress should focus on scientific and technological innovation, policy support and social engagement to promote the sustainable development of biomass-derived moulded fuels for a clean, renewable energy future. The potential of biomass forming fuels as a sustainable energy source is huge, and future development will require technological advances and equipment upgrades. EPCB Boiler as a supplier can provide more possibilities for the sustainable utilisation of biomass forming fuels and promote their wide application in the energy sector through continuous improvement of product features and technical performance.
FAQ
What is biomass briquette fuel?
Biomass briquette fuel is a solid fuel processed from biomass feedstocks, usually in the form of pellets or blocks. These biomass feedstocks can include wood chips, straw, discarded crops, wood waste, etc., which are processed to form combustible pellets or lumps. Widely used for heating, power generation, and industrial production, biomass molded fuels are regarded as a renewable energy source and are considered a carbon-neutral form of energy as the amount of carbon dioxide released during combustion is comparable to the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by the virgin material.
How can biomass briquette fuels help reduce pollution?
Reduced air pollutant emissions: Compared to traditional fuels such as coal and oil, biomass molded fuels release fewer pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx), during the combustion process. This reduces the concentration of harmful particles and gases in the air and reduces the level of air pollution.
Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: The amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) produced during the combustion of biomass molding fuels is sustainable relative to fossil fuels. Therefore, the use of biomass molding fuels reduces greenhouse gas emissions and contributes to the fight against global climate change.
Promoting sustainable energy development: Biomass molded fuels are a renewable energy source and their production process has a relatively low environmental impact. Promoting the use of biomass-forming fuels, can reduce dependence on limited fossil fuel resources and promote a shift in the energy mix towards a cleaner and more sustainable direction.
What are the types of boilers that can use biomass briquette fuels?
Fixed Grate Boilers: Fixed grate boilers are a common type of boiler that combusts biomass-forming fuel by placing it on a fixed rate with an air supply from below.
Chain Grate Biomass Boiler: The chain grate is a more common form of biomass boiler, where the biomass fuel is fed into the furnace chamber for combustion through a continuously moving chain. Chain grate is suitable for burning all kinds of well-formed biomass fuels, such as biomass pellets, stick fuels, etc., with a good degree of automation and high combustion efficiency.
Reciprocating grate biomass boiler: the grate piece of this kind of boiler will do reciprocating movement, by pushing the material forward and turning the material, to facilitate the good mixing of air and fuel and full combustion. The reciprocating grate is also suitable for molding biomass fuel within a certain particle size range and helps to improve combustion efficiency and reduce incomplete combustion products.
Fluidized bed boilers: Fluidised bed boilers use fluidized bed technology, where the particulate matter in the fuel bed is combusted in a fluidized state by injecting air into the bed. This design allows for higher combustion efficiencies and lower emission levels.
Co-firing system: A system in which biomass-derived molded fuels are used in conjunction with other conventional fuels, such as coal or natural gas. These systems are typically used in existing coal-fired boilers to co-fire biomass-forming fuels by adjusting the fuel ratio.
Each of these boiler types has its characteristics, and the right type can be selected for use according to specific needs and conditions. The wide applicability of biomass-forming fuel makes it useful in many types of boilers, providing a diverse range of options for clean energy utilization.
What are the main challenges in adopting biomass briquette fuels?
Unstable feedstock supply: The production of biomass molded fuels relies on biomass feedstocks such as wood chips, straw, etc. The supply of these feedstocks is subject to seasonal variations, climatic conditions, and crop harvests, and may be unstable.
High technology and equipment requirements: The production and utilization of biomass-forming fuels require the support of relevant technologies and equipment, such as biomass pellet mills and boiler retrofits. However, some of these technologies and equipment may require high-cost inputs and may not be readily available in some areas.
Land use conflicts: The production of biomass molding fuels may lead to competition for land, especially in some resource-poor areas, which may trigger land use conflicts. This may not only affect the availability of biomass feedstock but may also hurt local communities and ecosystems.
 Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler