Biomass fired boiler is a type of boiler that uses organic materials as fuel, and generates heat energy and steam by burning biomass (such as wood, crop residues, animal wastes, etc.). This kind of boiler is widely concerned because of its renewability and relatively low carbon emission. Biomass fuel has a wide range of sources, including sawdust, straw, rice husk and other agricultural and industrial by-products, making it an economical and environmentally friendly energy choice. Compared with traditional coal-fired or oil-fired boilers, biomass boilers can not only reduce the use of fossil fuels, but also improve combustion efficiency and reduce pollutant emissions through appropriate combustion control technologies. With the development of technology, chemical Biomass fired boiler combines efficient combustion technology and optimized chemical reaction process, which further improves energy conversion efficiency and makes it more competitive in industrial and commercial applications.
Boiler efficiency is a key index to measure boiler performance, which determines the ratio of fuel energy to available heat energy. Efficient boilers can minimize fuel consumption and improve energy utilization, thus reducing operating costs and environmental impact. In the process of energy production, boiler efficiency directly affects the economy and sustainability of the whole system. For example, efficient boilers can not only reduce the emission of carbon dioxide and other pollutants, but also help enterprises comply with environmental protection regulations and reduce carbon taxes and energy expenses. For biomass boilers, improving boiler efficiency means burning biomass fuel more fully, reducing incomplete combustion residues and improving heat recovery capacity. Especially in the context of the current global energy structure transformation to renewable energy, the improvement of boiler efficiency is very important to reduce the dependence on fossil energy and promote the development of green energy. Therefore, when evaluating the performance of different types of boilers, efficiency not only affects the economic benefits of enterprises, but also determines their environmental benefits and market competitiveness to a great extent.

Understand Boiler Efficiency

Definition and significance of boiler efficiency
Boiler efficiency refers to the boiler's ability to convert the energy contained in fuel into usable heat energy, usually expressed as a percentage. Its calculation methods mainly include direct efficiency method (based on the ratio of heat input and output) and indirect efficiency method (based on the analysis of various energy losses). Efficient boilers mean higher fuel utilization rate, thus reducing operating costs, reducing energy waste and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The improvement of boiler efficiency can not only improve the economy of industrial production, but also be an important way to realize sustainable energy management.
Factors affecting boiler efficiency
Boiler efficiency is affected by many factors, including:
Fuel characteristics: Different kinds of fuels have different combustion values and water contents, which directly affect the combustion efficiency. For example, biomass fuel with high humidity will reduce the efficiency of the boiler because extra heat is needed to evaporate water during the combustion process.
Combustion technology: advanced combustion technology (such as fluidized bed combustion or gasification combustion) can improve the combustion efficiency of fuel, reduce unburned residue and improve the overall thermal efficiency of boiler.
Air supply control: accurate control of air supply is very important for combustion process. Excessive air will increase heat loss, while insufficient air may lead to incomplete combustion and affect the overall efficiency of the boiler.
Heat exchange system: An efficient heat exchanger can maximize the use of heat energy generated by combustion, improve heat transfer efficiency and reduce heat loss.
Exhaust smoke loss: The higher the temperature of the exhaust gas discharged from the boiler, the greater the heat loss. Using economizer or preheater can effectively reduce the exhaust gas temperature and improve the overall efficiency of the boiler.
Overview of chemical biomass fired boiler
Chemical Biomass fired boiler is an advanced boiler type based on traditional biomass boiler, which combines chemical reaction to optimize combustion process and improve energy efficiency and fuel utilization. This kind of boiler usually adopts catalytic combustion, gasification combustion or other chemical processes to improve the combustion completeness of fuel and reduce pollutant emissions.
What is a chemical biomass fired boiler?

Common types and working principles
Chemical biomass boiler is a kind of biomass boiler which combines chemical reaction to optimize combustion process. The main types include:
Fluidized bed boiler (CFB): Use high-temperature granular bed to achieve high-efficiency combustion and improve fuel utilization.
Gasification boiler: converts biomass fuel into combustible gas and then burns it, which improves combustion efficiency and reduces particulate matter emission.
Catalytic combustion boiler: use catalyst to promote combustion reaction, improve low-temperature combustion efficiency and reduce pollutant emission.
Efficiency of chemical Biomass fired boiler
Chemical Biomass fired boilers can improve the utilization rate of heat energy by optimizing the combustion process, which is usually more efficient than traditional biomass boilers.

Its features include:
Adopt efficient combustion technology to reduce unburned materials and improve fuel conversion rate.
Combined with chemical reaction control, heat exchange efficiency is improved and heat loss is reduced.
Advanced flue gas treatment system can reduce the heat loss of flue gas and improve the overall thermal efficiency.
Typical Efficiency Range and Influencing Factors
The thermal efficiency of chemical biomass burning boilers is usually between 80% and 95%, depending on the following factors:

Fuel quality: Fuel with low moisture and high calorific value can improve combustion efficiency.
Boiler design: optimized combustion chamber structure, heat exchange system and flue gas circulation can reduce energy loss.
Operation and maintenance: Regular cleaning of boilers and optimization of combustion control can maintain efficient operation.
Advantages of using chemical biomass in boilers

High efficiency and energy saving: Compared with the traditional biomass boiler, the combustion is more complete and the heat energy utilization rate is higher.
Environmental protection and emission reduction: reduce particulate matter and harmful gas emissions, in line with environmental protection standards.
Fuel economy: the price of biomass fuel is lower, and the long-term operating cost is more competitive.
Renewable: reduce dependence on fossil fuels and promote sustainable energy development.
Comparison With Other Types of Boilers
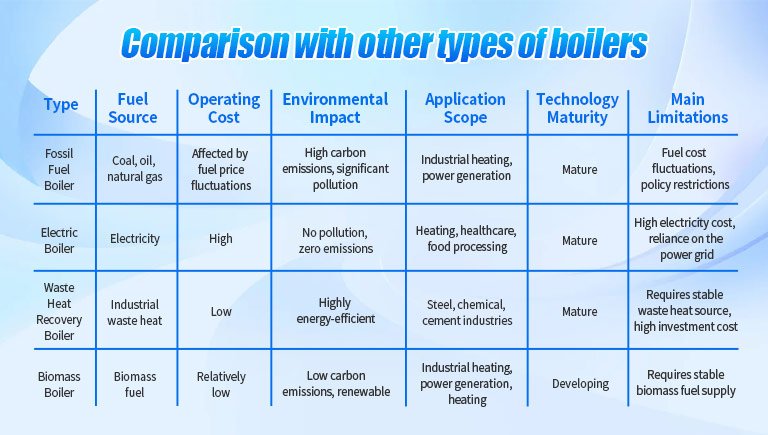
1. Fossil fuel boilers (coal, oil and natural gas)
Advantages:
High combustion efficiency: Modern fossil fuel boilers adopt advanced combustion technologies, such as low-nitrogen combustion and high-efficiency heat exchange, which improve the thermal efficiency, generally reaching 80%-95%.
Stable fuel supply: Coal, oil and natural gas are the main energy sources in the world, with perfect supply system and convenient fuel acquisition.
Mature technology: After long-term development, fossil fuel boilers are mature in design, manufacture, operation and maintenance, with high reliability.
Disadvantages:
Fuel cost fluctuates greatly: influenced by international market and policies, the prices of coal, oil and natural gas fluctuate greatly, and the operating cost is unstable.
High carbon emission and serious environmental pollution: A large number of carbon dioxide (CO), sulfur dioxide (SO), nitrogen oxides (NOx) and dust are produced in the combustion process, which has a significant impact on air quality and climate change.
Not in line with the sustainable development trend: under the goal of global carbon neutrality, countries gradually reduce the use of fossil fuels, and future policies may limit their application.
Comparison with chemical biomass fired boiler:
Compared with chemical biomass fired boilers, the carbon emission is lower, because the CO emission in the process of biomass combustion can be absorbed by photosynthesis in the process of biomass growth, thus achieving the effect of carbon neutrality. At the same time, it is more renewable, and biomass fuels are widely available, such as agricultural and forestry wastes, straws, sawdust, etc., while fossil fuels are non-renewable resources. In the long run, the operating cost of biomass boilers may be more advantageous, especially in areas with abundant biomass resources and policy support.
2. Electric boiler
Advantages:
Zero emission: No pollutants such as CO and SO are discharged during operation, which is environmentally friendly.
Simple operation: no complex combustion control system is needed, the start and stop are rapid, and the operation is highly intelligent.
Low maintenance cost: there is no combustion process, which reduces the wear of flue, combustion chamber and other parts, and the maintenance workload is small.
Quiet operation: no combustion noise, especially suitable for occasions requiring low noise.
Disadvantages:
Higher cost of electricity: the price of industrial electricity is higher, especially in high energy-consuming industries, and the long-term operation cost is higher.
Depend on the stability of the power grid: If the power supply is unstable or the cost fluctuates greatly, it may affect the economy and reliability of the boiler.
The initial investment may be large: high-power electric boilers need to be equipped with special power facilities, such as transformers and special cables, so as to increase the initial investment.
Limited energy conversion efficiency: thermal power plants can usually only achieve 30%-50% efficiency, while boilers that directly burn fuel have higher thermal efficiency, so overall, the energy utilization rate of electric boilers is relatively low.
Comparison with chemical biomass boiler:
Biomass fired boiler is more suitable for large-scale industrial application than electric boiler, because the high operating cost of electric boiler limits its application in high power demand occasions. At the same time, biomass fired boilers have a wider scope of application and can meet various heating needs, while electric boilers have higher requirements for power supply and are limited in areas with unstable power grids or expensive electricity bills. In addition, biomass fired boilers are more energy independent and can use a variety of fuels, while electric boilers are completely dependent on the power grid.
3. Waste heat recovery boiler
Advantages:
High energy utilization rate: By recycling industrial waste heat (such as boiler tail gas, smelting flue gas, steam turbine exhaust, etc.), energy waste is reduced and the overall efficiency of the system is improved.
Reduce waste heat emission: reduce waste heat emission in industrial process and reduce thermal pollution to the environment.
Reduce production cost: use waste heat to replace part of new fuel consumption and reduce energy expenditure.
Disadvantages:
Rely on industrial waste heat sources: there must be stable high-temperature waste heat sources, such as steel plants, cement plants, chemical plants, etc., which cannot operate independently.
Limited scope of application: mainly suitable for energy-intensive industries, but difficult for ordinary small and medium-sized enterprises or decentralized heating scenarios.
High initial investment: customized design is required, involving waste heat recovery equipment, heat exchanger, flue reconstruction, etc., with large initial investment and long recovery period.
Comparison with chemical biomass fired boiler:
Chemical biomass fired boilers can operate independently, while waste heat recovery boilers need to rely on other industrial waste heat sources. The combination of the two can improve the energy utilization rate, and the biomass boiler can be used as an auxiliary heat source of the waste heat recovery system to provide additional heat energy when the waste heat supply is insufficient, so as to realize efficient operation. In addition, biomass fired boilers are more suitable for distributed heating or small and medium-sized enterprises, while waste heat recovery boilers are more suitable for large industrial enterprises.
Case Study and Practical Application
Biomass-fired boilers have been widely used around the world in recent years, especially in energy-intensive industries, areas supported by renewable energy policies and countries rich in fuel resources.
1. Examples of biomass-fired boilers in industry
(1) Food processing industry: a dairy processing factory in Thailand.
A large dairy production enterprise in Thailand originally used natural gas boilers, but due to the rising fuel prices, the company decided to adopt a more environmentally friendly and lower-cost heating scheme.
The enterprise installed a 10-ton/hour biomass boiler, using sawdust and agricultural and forestry wastes as fuel to replace the original natural gas boiler.
Results:
Fuel cost reduction: Compared with natural gas, the cost of biomass fuel is reduced by about 30%.
Carbon emission reduction: the average annual reduction of CO emission is about 15,000 tons, which is in line with the EU carbon emission reduction policy.
Sustainability enhancement: through cooperation with local wood processing plants, the stable supply of biomass fuel is ensured, and the development of regional circular economy is promoted.
(2) Paper industry: a paper mill in Vietnam.
A paper mill in Vietnam used to use coal boilers. Because the local government tightened the restrictions on the use of coal, and a large amount of biomass waste (such as sawdust and pulp residue) was produced during the paper making process, the enterprise decided to use these wastes as fuel to replace the traditional boilers.
A 20-ton/hour biomass fluidized bed boiler is installed, and biomass wastes such as sawdust and straw during papermaking are used as the main fuel.
Results:
Reduce fuel costs: reduce the cost of coal procurement, saving about $2 million a year.
Reduce the cost of waste treatment: convert biomass waste into energy, avoiding the cost and pollution problems of waste landfill treatment.
Improve energy efficiency: the thermal efficiency of the boiler reaches 85%, which is higher than that of the traditional chain boiler (about 75%).
2. Comparative analysis of biomass boiler and other boiler types
(1) Comparison with fossil fuel boilers
Contrast dimension | Biomass boiler | Coal boiler | Oil/gas boiler |
Fuel cost | Relatively low (according to local conditions) | Traditionally, it is low, but it is greatly influenced by policies. | The price fluctuates greatly and the operating cost is high. |
carbon dioxide emission | Low, carbon neutrality can be achieved. | High, serious carbon emissions | High, natural gas is relatively low, but there are still carbon emissions. |
policy support | Many countries have subsidies and tax incentives. | Tend to be strict, and some countries restrict their use. | Gradually replaced by renewable energy. |
area of application | Heating, steam, power generation | Mainly used for high-temperature heating and power generation. | Suitable for small and medium-sized enterprises, heating and so on. |
Environmental protection performance | Low emission, in line with the trend of sustainable development. | The pollution is serious, and the desulfurization and denitrification equipment increases the extra cost. | Relatively clean, but there are still carbon emissions. |
(2) Comparison with electric boilers
Contrast dimension | Biomass boiler | Electric boiler |
Fuel source | Biomass (renewable resources) | Electricity (grid-dependent) |
running cost | Low, depending on the price of biomass fuel | High, especially high power demand scenarios |
Energy independence | Strong, can use a variety of biomass fuels. | Weak, completely dependent on the power grid |
carbon dioxide emission | Low, carbon neutral. | Depending on the power source (such as thermal power, indirect carbon emissions are high) |
area of application | Suitable for medium and large industrial enterprises. | Suitable for small heating, medical treatment, food processing, etc. |
(3) Comparison with waste heat recovery boiler
Contrast dimension | Biomass boiler | Waste heat recovery boiler |
Energy source | Independent biomass fuel | Rely on industrial waste heat |
area of application | Independent heating or combined with other boilers | Suitable for scenes where there is a lot of waste heat in industrial processes. |
cost of investment | medium | High, relating to waste heat recovery equipment. |
operational mode | Can run independently | Need to cooperate with the main heat source. |
Conclusion
Chemical biomass fired boilers realize low-carbon emission and energy sustainability through efficient utilization of renewable biomass fuel, which is suitable for industrial heating, power generation and heating. Its operating cost is low, which is suitable for high power demand, and can be used as a supplementary heat source of waste heat recovery system to improve energy utilization. Compared with fossil fuel boilers, it is more environmentally friendly; Compared with electric boilers, the cost is more advantageous; Compared with the waste heat recovery boiler, the operation is more independent.
As a key component of sustainable energy solutions, chemical biomass-fired boilers have environmental benefits, economic feasibility and energy security. In the future, with the optimization of combustion technology, the improvement of fuel supply chain and the increase of policy support, biomass boilers will play a more important role in the transformation of global energy structure and provide strong support for the realization of green and low-carbon development and energy diversification.
 Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler