Industrial boiler is the core equipment in many industries, which provides vital heat energy and steam for many processes. From driving production equipment to generating electricity, the boiler plays an indispensable role in industrial production. It provides steam or hot water by converting fuel into heat energy to meet the needs of all walks of life for heat energy. Whether it is heating, sterilization, power generation or chemical treatment, boilers provide a solid guarantee for efficient and stable production.
As a senior boiler manufacturer, EPCB boiler will deeply discuss the key role of boilers in industrial applications, analyze its working principle in detail, and focus on its specific applications in textile, food processing, pharmaceutical and chemical industries. By understanding the functions of industrial boilers, enterprises can better understand their value and explore effective ways to improve production efficiency and reliability.
What is a Boiler?
Boiler is a kind of equipment that converts fuel or other energy into heat energy. Its main function is to heat water and convert it into steam or hot water. Through efficient combustion and heat exchange, boilers can generate enough heat to meet various industrial and commercial needs. Steam boilersare mainly used to generate high-temperature and high-pressure steam, while hot water boilers are used to provide continuous hot water supply. Regardless of the type, the core goal of the boiler is to efficiently convert the chemical energy or electric energy of the fuel into usable heat energy.

Boilers play the following key roles in industry:
Heating: boilers provide heat energy for industrial facilities, which is used for heating in factory environment and heating demand in industrial processes. For example, the food processing industry needs boilers to provide heat for cooking, sterilizing and drying food.
Driving equipment: In many industrial fields, high-pressure steam generated by boilers is used to drive mechanical equipment, such as steam turbines, pumps and compressors. This is one of the core applications of power plants and some manufacturing industries.
Support production process: boilers play an indispensable role in industrial production. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, the steam generated by boilers is used to clean and sterilize equipment; In the textile industry, steam is used for fabric treatment and dyeing; In the chemical industry, the boiler heat energy supports the chemical reaction.
Through these functions, the boiler has become the core equipment of many industrial processes, and its reliability and efficiency directly affect the productivity and energy cost of enterprises. For this reason, it is very important for enterprises to choose a boiler with stable performance and high energy efficiency.
Types of Industrial Boilers and Their Applications
Industrial boilers can be divided into many types according to different designs and functions, and each type has unique advantages in specific scenarios.
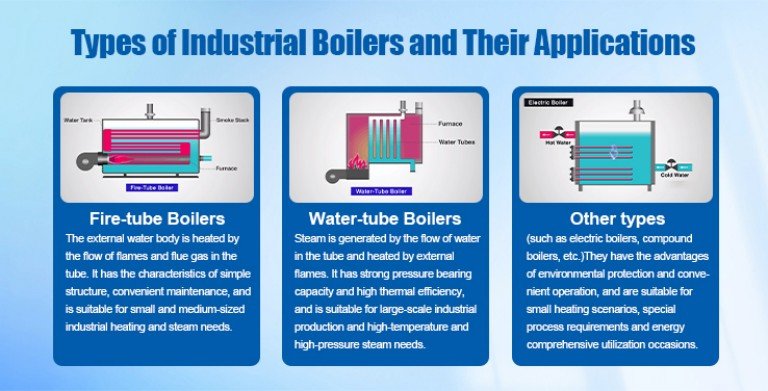
Fire-tube Boilers
Fire tube boilers generate steam by letting high-temperature flue gas flow through pipes arranged in water and transferring heat to surrounding water. The inside of a boiler usually consists of a large water tank and several smoke pipes, and the hot smoke generated by the combustion chamber passes through these smoke pipes to transfer heat energy to the water in the water tank.
Characteristic
Simple structure: the design of fire tube boiler is more traditional and easy to manufacture and maintain.
Stable operation: it is suitable for the production of medium and low pressure steam, and the operation is relatively stable.
Good economy: the initial investment cost is low, which is suitable for scenes with stable steam demand.
Industrial Applications
Fire tube boilers are widely used in industries that need medium and low pressure steam, such as food processing (cooking and sterilization), textile industry (dyeing and cleaning), small chemical plants and so on.
Water-tube Boilers
Water-tube boilers generate steam by letting water flow in tubes and being heated by high-temperature flue gas generated by external combustion. Contrary to the fire tube boiler, the water flow of the water tube boiler forms a network through multiple tubes, while the high temperature flue gas flows around the tubes.
Characteristic
Strong pressure-bearing capacity: Water-tube boiler can bear higher pressure, which is suitable for scenes requiring high-temperature and high-pressure steam.
High efficiency: Because the heat exchange area of water tube boiler is larger, the thermal efficiency is higher than that of fire tube boiler.
Strong adaptability: it can handle a variety of fuels, including coal, oil, natural gas and biomass fuel.
Industrial Applications
Water-tube boilers are mainly used in large industrial fields, such as power plants (driving steam turbines), petrochemical industry (heating and distillation), pharmaceutical industry (sterilization and process heat sources), and large factories that need high-efficiency and high-capacity steam supply.
Related Posts:The Differences Between Industrial Fire Tube Boiler & Water Tube Boiler
Other Types of Boilers
Electric energy is used to heat the resistance element, thus heating water into steam or hot water.
Advantages: no pollution, simple installation, suitable for small industries or places with high environmental protection requirements.
Industrial Applications: laboratories, hospitals, electronic manufacturing industries and other places that need clean energy.
Compound boiler
It combines the advantages of fire tube and water tube boiler, and has the characteristics of both.
Advantages: high efficiency and energy saving, suitable for various working conditions.
Industrial Applications: shipbuilding industry, large-scale industrial projects and other environments that need a variety of steam demand.
Using biomass fuel (such as sawdust, straw and rice husk) to generate heat energy.
Advantages: strong environmental protection, low fuel cost and low carbon emission.
Industrial Applications: Paper mills, food processing plants and other industries that pay attention to environmental protection and renewable energy.
Industrial Applications of Boilers
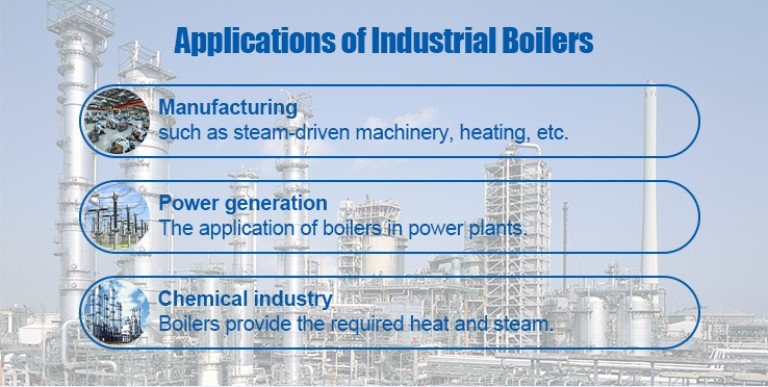
Manufacturing industry
In manufacturing industry, steam is an important power source to drive mechanical equipment. For example, steam turbines and compressors play a key role in factory production lines, and industrial boilers provide efficient and stable steam power for these devices.
Heat supply and heating
The manufacturing industry needs boilers to provide heat energy for production processes, such as:
Food processing: boilers are used for cooking, sterilization, drying and cleaning.
Textile industry: The steam generated by boilers is used for fabric dyeing, ironing and post-treatment.
Wood processing: boilers provide heat energy for wood drying to ensure product quality.
Production of industrial products
Many manufacturing products, such as rubber, plastics, metal products, etc., need to complete specific processes, such as heating, molding and melting, through high-temperature steam provided by boilers in the production process.
Power production
Industrial boiler is one of the key equipment in power plant, which generates high-temperature and high-pressure steam by burning fuel (such as coal, natural gas or biomass) to drive steam turbine to generate electricity. This process is the basis of traditional thermal power generation and some renewable energy power generation.
Cogeneration of heat and power (CHP) system
Many modern power plants adopt cogeneration system. Boilers are not only used to generate electricity, but also provide hot water or steam for surrounding industrial facilities or residential areas through waste heat recovery. This way greatly improves the efficiency of energy utilization and reduces energy waste.
Fuel adaptability
In the power industry, boilers can adapt to a variety of fuels according to demand, such as high-efficiency coal-fired boilers for large-scale power generation, gas-fired boilers for flexible power generation, and biomass boilers for green energy power generation projects.
Chemical industry
The chemical industry has a huge demand for heat energy, and the high-temperature heat energy provided by the boiler is used to support the chemical reaction. For example, in the production of refined petroleum, synthetic materials and chemicals, the heat of the boiler is the core power of catalytic and cracking reactions.
Supply process steam
Distillation and purification: the steam generated by the boiler is used for distillation and purification of materials in the chemical process.
Drying and evaporation: Many chemical products need steam drying to ensure their quality.
Sterilization and cleaning: The cleaning and sterilization of chemical equipment also depends on the high-temperature steam provided by the boiler.
Energy support for various processes
Many types of boilers are used in chemical industry, including water tube boilers and hot oil boilers, to meet the demand of accurate temperature control and continuous and efficient heat supply. These boilers play an important role in improving production efficiency and ensuring product quality.
Efficiency and Energy Saving of Boiler
Boiler efficiency is the core index to measure the performance of boiler equipment. Efficient operation of boilers can not only reduce energy consumption, but also reduce operating costs and environmental pollution. How to improve boiler efficiency? How to save energy by maintaining and optimizing operation? These problems deserve our deep thought.

Methods to improve boiler efficiency
Efficient combustion technology
Optimize the burner design: adopt advanced burner technology (such as low nitrogen burner) to ensure the full mixing of fuel and air, reduce the loss of incomplete combustion and improve the fuel utilization rate.
Accurate combustion control: Real-time monitoring of combustion state through automatic combustion control system (such as oxygen content control and combustion load adjustment) to maintain the best air-fuel ratio and maximize combustion efficiency.
Heat recovery technology
Use Economizer: install economizer to recover waste heat from boiler tail gas, which is used to preheat boiler feed water or air and improve the overall thermal efficiency of the boiler.
Waste heat recovery system: the waste heat recovery device (such as air preheater or heat exchanger) is used to convert the heat in waste gas into reusable energy.
Condensation recovery technology: For steam boilers, the condensate recovery system is installed to send the condensate back to the boiler, which not only saves heat energy, but also reduces the waste of water resources.
Optimize boiler structure and operation parameters.
Improve the heat exchange area of the boiler and reduce the heat loss by optimizing the heat transfer structure.
Reasonable setting of boiler operation parameters, such as increasing steam pressure or reducing exhaust temperature, can achieve higher efficiency.
Reduce energy waste through regular maintenance and optimized operation.
The importance of regular maintenance
Cleaning boiler equipment: The scale and dirt on the heating surface of the boiler will significantly reduce the heat transfer efficiency, and cleaning the heat exchange surface regularly can effectively improve the thermal efficiency.
Check the combustion system: check the burner, fan and fuel nozzle regularly to ensure that the fuel burns fully and reduce unnecessary energy consumption.
Monitoring exhaust temperature: High exhaust temperature usually means heat energy loss, and regular inspection and adjustment of exhaust system can reduce energy waste.
Optimize boiler operation
Regularly calibrate instruments, such as pressure gauge, thermometer and flowmeter, to ensure that the boiler is always in the optimal operation state.
Training operators: improve the skills of boiler operators to ensure that they can make reasonable adjustments according to production requirements and boiler performance.
Load optimization management: scientifically distribute boiler load according to production demand to avoid long-term operation of boiler under inefficient load.
Digital management and monitoring
Intelligent control system: By introducing boiler management software, real-time monitoring and automatic adjustment can be realized, and energy waste caused by human error can be avoided.
Data analysis and optimization: analyze the boiler efficiency and fuel consumption trend by using operation data, find potential problems and optimize operation strategy in time.
Common Boiler Problems and Maintenance
During the long-term operation of the boiler, various common problems may occur, which will affect its efficiency and safety. Therefore, it is very important to understand common problems and implement effective maintenance measures. The following are detailed from two aspects: common problems and maintenance suggestions.

Common Boiler Problems
Pressure is unstable
Problems: During the operation of the boiler, the pressure of steam or hot water fluctuates or cannot be kept stable.
Possible reasons:
Combustion control system failure, resulting in insufficient or excessive fuel supply.
The exhaust valve or safety valve is not tightly sealed, resulting in steam leakage.
The load demand fluctuates greatly, and the boiler fails to adjust the operation parameters in time.
Impact: Unstable pressure will lead to uneven heat energy supply, affect the production process, and at the same time may cause overload operation of boiler equipment and increase safety risks.
Water quality management
Problems: scaling, corrosion or poor water circulation in the boiler.
Possible reasons:
The inlet water quality is not up to standard, and the hardness and impurity content are too high.
Lack of effective water treatment equipment (such as softener and deaerator).
Failure to discharge pollutants regularly leads to the accumulation of solid impurities in boiler water.
Impact: Water quality problems will reduce boiler thermal efficiency, increase fuel consumption, shorten equipment life, and even cause pipeline leakage or burst accidents.
Incomplete combustion
Problem: The flue gas after fuel combustion contains more unburned components, such as carbon monoxide or black smoke.
Possible reasons:
The burner is not properly adjusted, and the ratio of air to fuel is unbalanced.
Poor fuel quality or unsuitable for boiler design.
Ash accumulation or blockage in the combustion chamber affects the combustion efficiency.
Impact: It leads to energy waste, increased pollutant emission, and affects the overall performance of the boiler.
Maintenance suggestions
Regular inspection
Pressure and temperature inspection: regularly monitor whether the pressure and temperature of the boiler are within the normal range, find abnormal fluctuations in time, and avoid overload operation of the boiler.
Burner inspection: check the working state of the burner to ensure that the fuel nozzle and air passage are unobstructed.
Inspection of exhaust system: ensure that there is no leakage in the exhaust pipeline, and the exhaust temperature is within the normal range to avoid heat loss.
Cleaning and maintenance
Cleaning inside the boiler: remove the scale and dust on the heating surface regularly to improve the heat transfer efficiency. Especially for water tube boilers and fire tube boilers, it is very important to clean the pipes.
Flue cleaning: Clean up the accumulated dust in the flue regularly to avoid blocking and affecting smoke emission.
Cleaning of combustion chamber: remove the accumulated ash and unburned residue in the combustion chamber to ensure a clean combustion environment.
Water quality management
Installation of water treatment equipment: equipped with softened water equipment, deaerator, etc., to ensure that the inlet water quality meets the boiler operation standards.
Periodic blowdown: according to the operation situation, regularly discharge the sediment at the bottom of the boiler to prevent the accumulation of scale and impurities.
Water quality monitoring: regularly detect the hardness, pH value and dissolved oxygen content of boiler water to ensure that it meets the boiler design requirements.
Parts replacement
Replace wearing parts: such as seals, valves, pressure gauges, etc., regularly check and replace aging or damaged parts in time.
Burner maintenance: replace the nozzle or other worn parts of the burner to keep the combustion system running efficiently.
Calibration of sensors and instruments: regularly calibrate pressure gauges, thermometers and flowmeters to ensure accurate and reliable measurement data.
Professional maintenance and training
Regularly invite professional and technical personnel to conduct comprehensive inspection and debugging of boilers, find potential problems and repair them in time.
Provide training for boiler operators, ensure that they have correct operation skills and emergency handling ability, and reduce failures caused by human operation errors.
Conclusion
As the core power source of production equipment, industrial boilers play an irreplaceable role in manufacturing, power production, chemical industry and other fields. It not only provides efficient and stable heat and steam for industrial processes, but also supports key production links in many industries, such as heating, driving equipment and supporting complex chemical reactions. The versatility and wide application of industrial boilers fully reflect its importance to the development of modern industry.
However, the efficient operation and long-term reliability of boilers are inseparable from scientific management and maintenance. Adopting advanced combustion technology and introducing heat recovery devices can not only improve boiler efficiency, but also greatly reduce energy consumption and operating costs. At the same time, regular inspection and cleaning of the boiler, optimization of operation process and timely replacement of aging parts can effectively reduce the risk of equipment failure and prolong the service life of the boiler.
For enterprises, efficient operation of boilers is not only an important means of energy saving and emission reduction, but also the basis for improving production efficiency and ensuring production continuity.
EPCB boilers focus on providing efficient and environmentally friendly boiler solutions to meet diverse industrial needs. Choosing EPCB boiler is not only a commitment to quality, but also a step to promote a green future. Through correct boiler selection and optimized operation, enterprises can realize cost saving, improve productivity and maintain a leading position in the competition.
 Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler