1. The Importance of Daily Inspections for Oil-fired Boilers
Oil fired boilers play a critical role in chemical plants by providing a stable heat source essential for processes such as raw material heating, chemical reactions, and product purification, thus ensuring smooth production. Their high thermal efficiency and low operating costs are achieved by optimizing fuel usage and combustion processes, which helps reduce energy consumption and emissions, thereby lowering production costs. Despite their design to meet strict safety standards, regular inspections and maintenance are indispensable for ensuring production safety.
Daily inspections are crucial for maintaining the safety and efficiency of oil-fired boilers. Regular checks can prevent performance declines and safety incidents caused by issues such as fuel quality, combustion conditions, and water quality. They also help in promptly identifying and addressing problems such as leaks, corrosion, and scaling, which effectively mitigates potential risks. Moreover, regular inspections ensure continuous production by avoiding downtime caused by equipment failures, which is vital for output, quality, and economic efficiency. Additionally, inspections can enhance boiler efficiency by optimizing combustion parameters, removing soot and scale, and reducing energy consumption and emissions for greener, more efficient production.
Therefore, to maintain high operational efficiency and safety, it is crucial to establish and adhere to a detailed daily inspection checklist. EPCB Boilers, with their professional experience, offer comprehensive inspection checklists tailored for oil-fired boilers in chemical plants to ensure optimal performance in daily operations.
2. Basic Working Principle of Oil-fired Boilers
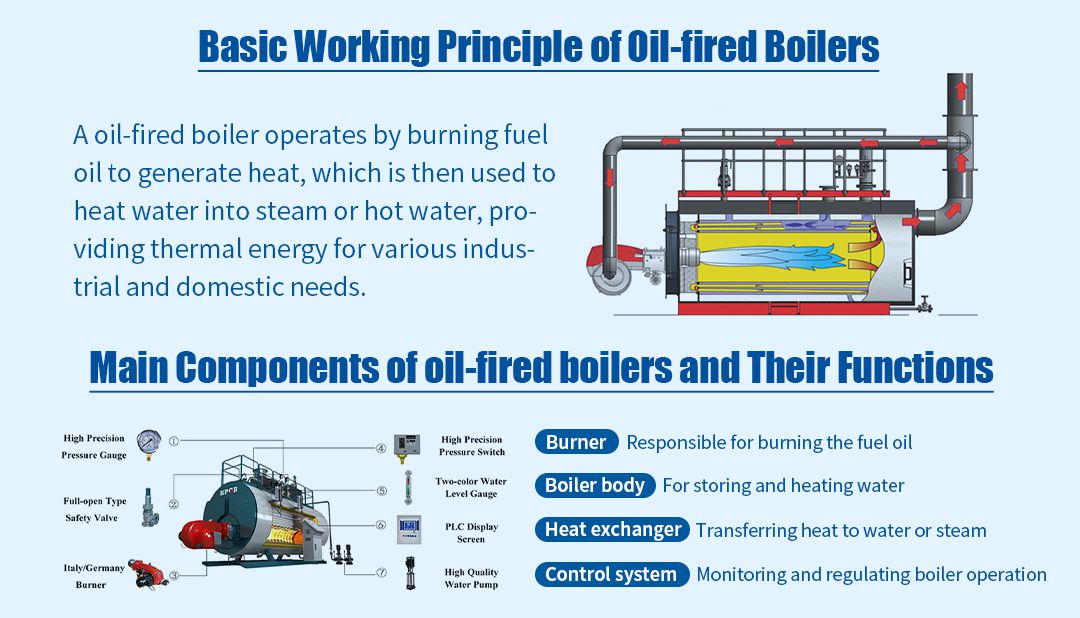
oil-fired boilers consist of several components: the combustion chamber, fuel pump, burner, ignition device, heat exchanger, control system, fuel tank, and flue. The combustion chamber burns the fuel to produce a flame, the fuel pump delivers fuel to the combustion chamber, the burner atomizes the fuel and mixes it with air, the ignition device starts the combustion, the heat exchanger transfers thermal energy, the control system regulates operation, the fuel tank stores the fuel, and the flue expels exhaust gases. These components work together to ensure stable operation of the boiler.
The working principle of a oil-fired boiler involves fuel supply, combustion, heat exchange, and control systems. The fuel pump transfers fuel from the tank to the combustion chamber, where it is atomized by the burner and mixed with air. The ignition device ignites this mixture, creating a flame that burns on the heat exchange surface, transferring heat to the medium to generate steam, hot water, or warm air. The control system monitors and adjusts the fuel flow, ignition, flame intensity, and temperature to ensure stable and efficient operation of the boiler, meeting the heating demands.
Common types of oil-fired boilers include fire-tube boilers and water-tube boilers. In fire-tube boilers, flames and flue gases flow inside the tubes while water flows outside, with heat exchanged through the tube walls. This simple structure results in lower thermal efficiency. In water-tube boilers, water flows inside the tubes while flames and flue gases flow outside, which enhances heat exchange efficiency and overall performance.
Fire-tube boilers require inspection to ensure the flue is clear to prevent smoke backflow, check for corrosion or wear on the tube walls, and maintain proper water levels to prevent accidents. Water-tube boilers should ensure smooth water circulation, prevent impurities and scaling, check that tube connections are tight and leak-free, and verify stable operation of the control system.
3. Daily Inspection Checklist for Oil-Fired Boilers
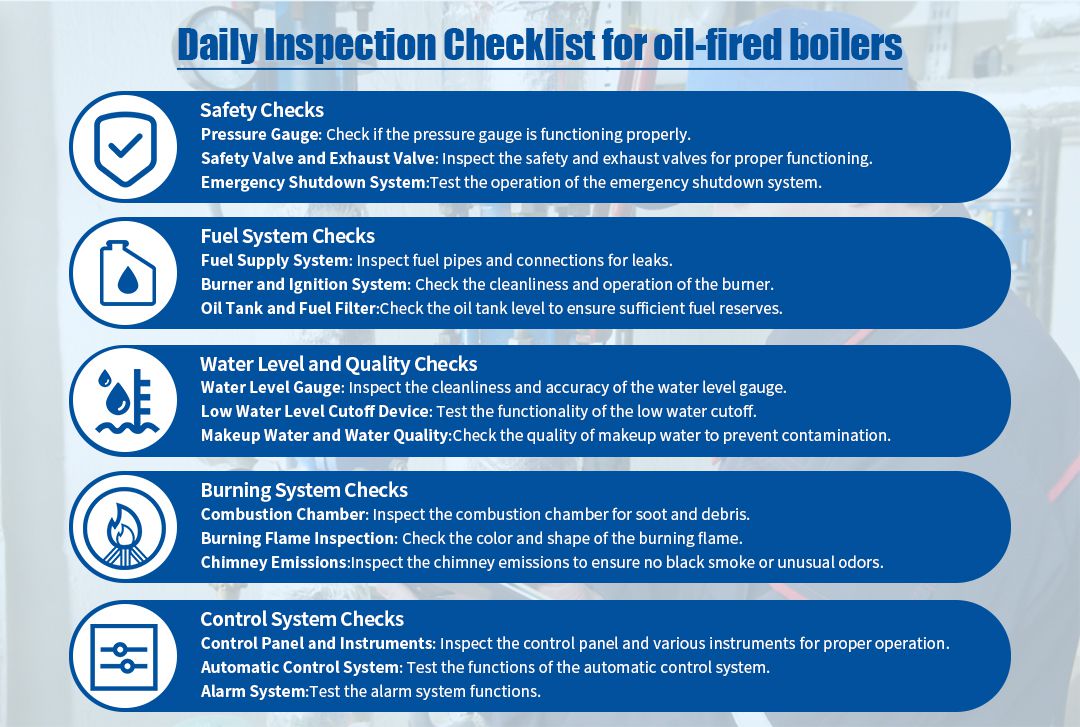
3.1 Safety Inspection
3.1.1 Pressure Gauge:
Inspect the pressure gauge to ensure it is functioning properly. Observe the movement of the needle to confirm it is not sticking or unstable. Check that the pressure readings are within the manufacturer's specified safety range. If the readings are outside this range, take corrective action immediately.
3.1.2 Safety Valves and Vent Valves:
Examine the safety and vent valves for signs of leakage or blockage. Manually operate the valves to ensure they can release pressure when needed and confirm there are no obstructions affecting their proper function.
3.1.3 Emergency Shutdown System:
Check all components of the emergency shutdown system to ensure they are functioning correctly. Simulate an emergency situation to confirm that the boiler and associated equipment can safely and promptly shut down.
3.2 Fuel System Inspection
3.2.1 Fuel Supply System:
Inspect the combustion chamber, removing any soot and debris to ensure it is clean. Verify that the combustion chamber is well-sealed with no air leaks. Regularly checking and maintaining the seal of the combustion chamber helps ensure complete fuel combustion, improving boiler efficiency and operational safety.
3.2.2 Burner and Ignition System:
Observe the flame color and shape to ensure it is stable and without flickering. Verify that the flame color is appropriate (typically blue). If the flame appears yellow or unstable, it may indicate incomplete combustion or improper air-fuel ratio, and adjustments to the burner settings should be made. Regular monitoring of the flame can enhance boiler efficiency and reduce pollutant emissions.
3.2.3 Fuel Tank and Fuel Filter:
Regularly check the fuel tank level to ensure adequate fuel reserves. If the fuel level is low, refill promptly. Also, inspect the fuel filter and clean or replace it as needed to prevent blockages from impurities and sediment, ensuring clean fuel for stable combustion and efficiency.
3.3 Water Level and Water Quality Inspection
3.3.1 Water Level Gauge:
Regularly check the cleanliness of the water level gauge to ensure it is transparent and free from dirt, allowing clear visibility of water levels. A dirty gauge may lead to inaccurate readings. Monitor the water level to ensure it remains within the specified safety range. Both high and low water levels can negatively impact boiler safety and operation.
3.3.2 Low Water Level Cutoff Device:
Regularly test the low water level cutoff device to ensure it responds promptly and shuts down the boiler when water levels fall below the safety line. Simulate low water level conditions to test the sensitivity and reliability of the device. Confirm that the device can effectively shut down the boiler to prevent dry firing or other hazardous conditions.
3.3.3 Make-up Water and Water Quality:
Regularly test the quality of make-up water to ensure it meets boiler operation standards, preventing scaling or corrosion inside the boiler. Pay special attention to the hardness, salt content, and pH levels of the water. Ensure that water treatment equipment, such as softeners, deaerators, and filters, is functioning properly and maintained regularly to effectively filter and treat impurities and harmful components in the make-up water.
3.4 Combustion System Inspection
3.4.1 Combustion Chamber:
Inspect the combustion chamber regularly, removing soot and debris to keep it clean and unobstructed. Verify that the combustion chamber is well-sealed to prevent air leaks and maintain efficient combustion.
3.4.2 Flame Inspection:
Observe the color and shape of the combustion flame to ensure it is stable and without anomalies. An ideal flame color is blue. If the flame is unstable or appears yellow or orange, adjust the air-fuel ratio or perform maintenance.
3.4.3 Chimney Emissions:
Inspect the chimney emissions to ensure there is no black smoke or unusual odors, indicating complete combustion. Verify that emissions meet environmental standards to avoid pollution. If abnormalities are detected, investigate and correct the issue promptly.
3.5 Control System Inspection
3.5.1 Control Panel and Instruments:
Inspect the control panel and various instruments to ensure they are operating correctly. Ensure all displayed data is accurate and regularly calibrate instruments to prevent reading deviations, allowing operators to monitor boiler status in real-time.
3.5.2 Automatic Control System:
Test the functions of the automatic control system to ensure its automatic control and adjustment functions are working correctly. This includes combustion control, water supply control, and other systems to ensure the boiler can automatically adjust operating parameters according to needs, improving efficiency and safety.
3.5.3 Alarm System:
Test the alarm system to ensure all alarm signals are emitted promptly. Simulate various fault conditions, such as high pressure, low water levels, or combustion abnormalities, to ensure the alarm system alerts operators in time to take necessary actions and prevent accidents.
4. Daily Inspection Records and Management

In boiler maintenance, systematic inspection records and management are crucial. They not only ensure the proper operation of boiler equipment but also effectively prevent potential faults and safety hazards. By meticulously documenting daily inspection details and discovered issues, we can track the boiler’s operational status and maintenance history, providing a basis for timely problem resolution.
4.1 Inspection Records:
Record the details of daily inspections and any identified issues, maintaining detailed inspection logs. Comprehensive logs aid future reference, track the boiler’s operating status and maintenance history, and facilitate the identification and analysis of potential problems.
4.2 Problem Handling:
Address issues discovered during inspections promptly and document the process and results of problem resolution. Ensure each issue is effectively resolved and maintain transparent and traceable records of the handling process.
4.3 Management and Supervision:
Regularly review inspection records to ensure the effectiveness of daily inspections. Management should periodically check and supervise to ensure inspections are thorough, ensuring the boiler operates safely and reliably. This management and supervision mechanism helps identify and resolve issues promptly, preventing accidents.
5. FAQ
Why is daily inspection of oil-fired boilers necessary?
Daily inspections of oil-fired boilers are essential for several reasons: safety, efficiency, longevity, and reducing faults. They ensure safe operation by preventing hazards from turning into accidents, enhance combustion and thermal efficiency to save energy and reduce emissions, extend equipment lifespan and reduce maintenance costs, and minimize unplanned downtime to ensure continuous production. Additionally, it is a compliance requirement, adapting to environmental changes and responding effectively to unforeseen situations to ensure stable and efficient operation.
What issues can daily inspections prevent?
Daily inspections are critical for the safe operation of oil-fired boilers, preventing faults and accidents while ensuring efficient operation and extending lifespan. Regular inspections help detect and address issues such as: the proper functioning of the fuel supply system to avoid disruptions or fuel quality problems affecting combustion; cleanliness of the combustion system to prevent soot and blockages affecting efficiency; the reliability of safety devices such as safety valves and pressure gauges; and the integrity of electrical system connections to prevent short circuits or leakage.
How to develop an effective daily inspection plan?
Developing an effective daily inspection plan is crucial for maintaining stable operation of equipment, systems, or environments. Start by defining the purpose (fault prevention, safety, efficiency) and scope (equipment, systems, areas, or processes) of the inspections. Gather information to analyze current conditions, historical issues, and potential risks, and identify inspection needs and priorities. Then, establish inspection content and standards, defining inspection items and criteria. Based on risk assessment, set reasonable inspection frequencies. Create an inspection schedule listing items, times, and responsibilities. During implementation, perform inspections on time, record results, and address issues promptly. Regularly review and adjust the plan as needed. Continuously improve by summarizing experiences, training personnel, keeping up with technological advancements, and adopting new tools to enhance inspection efficiency and accuracy.
Which professionals should be involved in daily inspections?
In daily inspections, the involvement of professionals varies by context: in manufacturing facilities, operators perform self-inspections, team leaders supervise, and safety engineers oversee overall control; in medical laboratories, management supervises, operational staff conducts inspections, and quality supervisors evaluate; in sectors such as construction, food, and environmental protection, it includes direct operators, management personnel, and specialists from various fields to ensure comprehensive and effective inspections.
What to do if a major issue is discovered?
If a major issue is discovered during daily inspections, promptly record the details, assess the severity, and report to higher management and relevant departments. Initiate an action plan to control risks, form a team to investigate thoroughly, and develop and execute a resolution plan. Afterward, summarize experiences, improve mechanisms, train personnel, and communicate the progress internally and externally.
6. Conclusion
The critical role of oil-fired boilers in chemical plants underscores the importance of daily inspections. Regular inspections are essential to ensure the safe operation and high efficiency of boilers, preventing potential faults and safety hazards. Daily checks cover various aspects, including safety inspections, fuel systems, combustion systems, control systems, and water levels and quality. Each of these components is crucial to the overall operation of the boiler.
The long-term benefits of adhering to daily inspections are clear. Regular checks help promptly identify and resolve equipment issues, reducing the likelihood of unexpected failures and extending the boiler's lifespan. They also enhance boiler efficiency, lower energy consumption, and reduce operational costs. Additionally, systematic recording and management provide detailed maintenance histories that support future maintenance decisions and improvements.
To achieve optimal inspection results and equipment performance, choosing the right boiler brand is crucial. EPCB Boilers, with their advanced technology and efficient combustion systems, offer reliable solutions for users. EPCB Boilers are designed with daily maintenance and inspection convenience in mind, making each check more efficient and accurate. We encourage plant managers to not only prioritize and implement daily inspection routines but also to select high-quality equipment partners to ensure that their production processes remain efficient, safe, and environmentally friendly. Feel free to contact EPCB Boilers for more information.
 Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler