Introduction to Energy-Saving Retrofits
In the chemical industry, optimizing energy utilization efficiency is crucial. It directly impacts the economic benefits, environmental friendliness, and long-term competitiveness of enterprises. Efficient energy use helps reduce production costs and greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with the trend of green chemistry.
To address this, retrofitting Oil/ Gas steam boilers becomes a key measure to enhance the energy efficiency of chemical plants. This retrofit involves multiple professional aspects, including adopting more efficient combustion technology, optimizing heat recovery systems, and introducing intelligent control systems. Specifically, replacing the fuel with cleaner energy sources (such as natural gas) and combining it with advanced combustion control strategies can significantly improve boiler thermal efficiency. At the same time, utilizing waste heat recovery technology can recycle the heat energy from flue gas, further reducing energy waste.

After implementing the retrofit of oil/gas steam boilers, companies can expect significant energy-saving effects and economic benefits. On one hand, the reduction in fuel costs will directly enhance the profitability of the enterprise. On the other hand, the improvement in boiler operating efficiency will promote the stability and safety of the production process, indirectly enhancing the company's market competitiveness. In summary, gas-fired steam boiler retrofits are an important way for chemical companies to achieve energy efficiency improvements and promote sustainable development.
Understanding Oil/Gas Steam Boilers

What is a Oil/Gas Steam Boiler?
A Oil/ Gas steam boiler refers to a steam boiler that uses fuel (such as diesel, heavy oil, etc.) or gas (such as natural gas, liquefied gas, city gas, etc.) as fuel. These boilers can be of a single fuel type, such as dedicated fuel steam boilers or gas steam boilers, or dual fuel types, which can burn both oil and gas. They release heat by burning these fuels to heat the water inside the boiler, vaporizing it into steam to meet the thermal energy needs of various industrial production and living purposes.
Basic Working Principle
The basic working principle of a oil/gas steam boiler is: the burner sprays fuel or gas into the furnace for combustion. The high-temperature flue gas generated by the combustion flows inside the boiler, transferring heat through the heat exchanger to the water in the boiler, raising its temperature and vaporizing it into steam. This steam is then transported through pipes to various thermal equipment to meet industrial production or heating needs.
Application and Role of Steam Boilers in Chemical Production
Steam boilers play a key role in chemical production, mainly for: providing thermal energy for heating and distillation of chemical raw materials and products, enabling purification or separation; regulating steam temperature and pressure to meet the temperature requirements of different reaction processes; and transferring heat to substances through heat exchangers for drying and dehydration.
In today's rapidly evolving chemical industry, technological iterations and rising environmental requirements have become irreversible trends. However, when we focus on those crucial oil/gas steam boilers responsible for heat conversion, an undeniable reality emerges: if these key devices are not subjected to necessary modifications and upgrades over time, they will inevitably face a series of severe challenges.
Unmodified oil/gas steam boilers often face issues like low efficiency, poor environmental performance, safety hazards, and poor adaptability. Low efficiency leads to energy waste and higher costs, and while gas boilers are cleaner than coal-fired ones, inadequate combustion and high pollutant emissions can still fail to meet stringent standards. Safety concerns such as incomplete combustion and leakage can disrupt operations, shorten lifespan, and endanger personnel and property. Additionally, with advances in chemical production technology, unmodified boilers may not meet new process requirements, resulting in inadequate or excessive thermal energy, affecting production efficiency and product quality.
Key Methods For Gas Fired Steam Boiler Retrofit
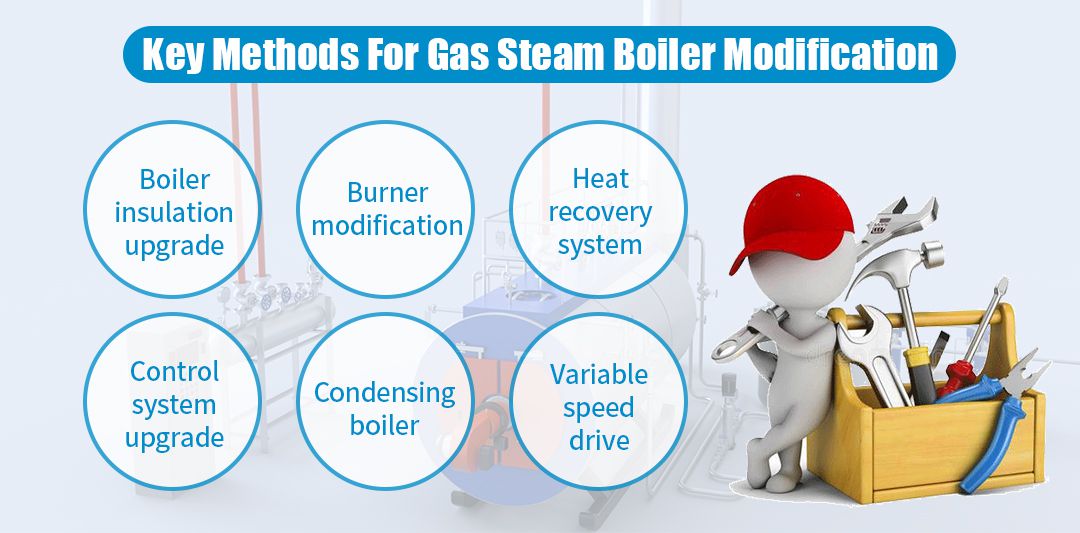
Retrofit of oil/gas steam boilers is a crucial measure to enhance energy efficiency, reduce operating costs, and minimize environmental impact. With a scientific retrofit plan, boilers can significantly improve efficiency, reduce energy consumption, optimize combustion processes, and effectively decrease pollutant emissions, ensuring environmental compliance. Additionally, retrofits can enhance equipment safety, extend service life, and ensure continuous and stable production. The following outlines several key retrofit methods to provide practical optimization paths for enterprises.
Boiler Insulation Upgrade: Insulation is a critical component of the boiler system. Proper insulation can effectively reduce heat loss, maintain the internal temperature of the boiler, thereby improving combustion efficiency and reducing fuel consumption. EPCB boilers typically use high-performance insulation materials such as fiberglass and mineral wool, which offer excellent thermal insulation and high-temperature resistance.
Burner Retrofit:EPCB boiler systems are equipped with burners that utilize low-NOx combustion technology, staged combustion, and oxygen-enriched combustion technology. These technologies can effectively improve combustion efficiency and reduce pollutant emissions.
Advantages in fuel efficiency include:
1.Staged Combustion and Air Premixing Technology: Reduces the formation of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and enhances combustion efficiency.
2.Intelligent Control System: Real-time monitoring of various parameters during the combustion process, automatically adjusting the burner's operating state to ensure optimal combustion.
Heat Recovery System:A heat recovery system can reuse waste heat generated during boiler operation, improving the overall thermal efficiency of the system and reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Types of heat recovery systems commonly used in EPCB boiler systems include:
1.Economizers: Installed at the boiler's exhaust, they recover residual heat from flue gases to preheat the boiler feedwater, increasing boiler thermal efficiency.
2.Condensate Recovery: Recovers heat from steam condensate, which can be used to preheat boiler feedwater or for other purposes, reducing energy waste.
Control System Upgrade:Modern control systems enable precise control and optimized adjustment of the boiler operation process, improving response speed and operational efficiency. Automation control systems can automatically adjust and optimize the boiler operation, reducing human error and ensuring the boiler always operates in the optimal state. Monitoring systems can provide real-time monitoring of various boiler parameters, promptly identifying and addressing anomalies, preventing energy waste and equipment damage, thus playing a crucial role in energy saving.
Condensing Boilers:Condensing boilers utilize condensing technology to recover latent heat from flue gases, increasing boiler thermal efficiency. The latent heat released during the condensation process is absorbed and utilized by the boiler, reducing fuel consumption. Condensing boilers offer high efficiency, low emissions, and stable operation, making them one of the most advanced boiler technologies available. When installing condensing boilers, attention must be paid to the design of the drainage system to ensure smooth discharge of condensate. Additionally, the boiler room must be well-ventilated to prevent equipment corrosion from condensate.
EPCB Case Study: Successful Energy-saving Retrofit

EPCB Boiler is a company specializing in boiler design, manufacturing, and retrofitting, with extensive experience and deep expertise. EPCB is renowned for its efficient energy-saving solutions and innovative technologies in boiler retrofitting, successfully helping numerous enterprises enhance their energy efficiency and reduce operating costs.
Project Background
The client for this project is a chemical plant facing high energy consumption, high operating costs, and excessive environmental emissions. The client aims to improve energy efficiency, reduce fuel consumption and operating costs, and decrease pollutant emissions to meet higher environmental standards through boiler retrofitting.
Provided Solutions
EPCB provided the chemical plant with a comprehensive boiler retrofit solution, which included the following aspects:
Boiler Insulation Upgrade: Utilizing high-performance insulation materials and advanced insulation technology to reduce heat loss.
Burner Retrofit: Introducing advanced burner technology—low NOx burners to improve combustion efficiency and reduce pollutant emissions.
Heat Recovery System: Installing economizers and condensate recovery systems to recover waste heat from flue gas and condensate, enhancing overall thermal efficiency.
Control System Upgrade: Implementing advanced automation control and monitoring systems to achieve precise control and optimization of boiler operation.
Condensing Boiler: Adopting condensing technology to recover latent heat from flue gases, improving overall boiler thermal efficiency.
Results and Benefits
Through the implementation of the above retrofit solutions, the chemical plant's energy efficiency significantly improved, with the following specific results:
Boiler thermal efficiency increased by more than 15%, and fuel consumption was significantly reduced.
Due to the reduction in fuel consumption and improvement in system operating efficiency, overall operating costs decreased by 20%.
The client expressed high satisfaction with EPCB boiler's retrofit solutions, noting that not only were the expected energy-saving goals achieved, but system stability and environmental performance were also significantly enhanced. The client's feedback attests to EPCB boiler's professional expertise and technical prowess in the field of boiler retrofitting.
Benefits of Retrofitting Gas Fired Steam Boilers

Retrofitting gas fired steam boilers not only significantly improves equipment efficiency, reduces energy consumption, and lowers operating costs, but also optimizes the combustion process, reducing pollutant emissions and ensuring compliance with strict environmental standards. Additionally, retrofitting enhances equipment safety, reduces failure rates, extends service life, and ensures continuity and stability of production. Through scientific retrofitting solutions, enterprises can achieve economic benefits while fulfilling social responsibilities and promoting sustainable development.
1. Energy Efficiency
Retrofitting gas fired steam boilers can significantly improve energy utilization efficiency and reduce fuel consumption, thereby lowering overall operating costs. By using advanced burner technology and heat recovery systems, boilers can more effectively utilize the heat from fuel, reducing energy waste.
Recently, a chemical plant improved its boiler thermal efficiency by over 15% and reduced fuel consumption by 20% through boiler insulation upgrades and burner retrofitting. This significant improvement in energy efficiency not only lowered operating costs but also reduced the negative impact on the environment.
2. Environmental Impact
Retrofitting gas-fired steam boilers can significantly reduce pollutant emissions, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon dioxide (CO2), and particulate matter. This not only helps improve air quality but also reduces greenhouse gas emissions, positively contributing to climate change mitigation.
Many countries and regions have strict regulatory requirements for industrial boiler emissions. By retrofitting boilers to improve combustion efficiency and reduce emissions, enterprises can ensure compliance with these environmental regulations, avoiding penalties for non-compliance.
3. Cost Savings
In the short term, retrofitting gas-fired steam boilers can lower fuel costs and maintenance expenses. In the long term, improved energy efficiency and extended equipment lifespan can bring continuous cost savings.
Although boiler retrofitting requires an initial investment, fuel cost savings and reduced maintenance expenses typically allow for a return on investment within 2-3 years. For example, a food processing plant installed a condensing boiler and heat recovery system, saving more in fuel costs within two years than the initial retrofitting investment.
4. Operational Efficiency
Retrofitted boilers usually have higher performance and reliability, reducing failures and downtime. Utilizing advanced control systems and automation technologies ensures the boiler operates in optimal condition, increasing production efficiency.
Modern boiler retrofitting solutions often include more efficient monitoring and automation systems that can detect the boiler's operating status in real-time, identify potential issues early, and reduce unexpected downtime and maintenance needs. For instance, the application of variable speed drives (VSD) can reduce mechanical wear on pumps and fans, extending equipment lifespan.
Implementation and Maintenance Considerations
Successful energy-saving retrofitting not only relies on advanced technology but also requires scientific implementation and meticulous maintenance. Precise execution of each step in the retrofitting process, including equipment selection, system design, and installation and commissioning, is crucial. In terms of maintenance, regular inspections and upkeep of retrofitted equipment are essential to ensure long-term stable operation, timely resolution of potential issues, extension of equipment lifespan, and continuity of production. Next, EPCB Boiler will discuss the implementation and maintenance considerations for energy-saving retrofitting of oil/gas-fired steam boilers in chemical plants in detail, helping enterprises avoid common problems and achieve optimal retrofit results.
1. Planning and Assessment
Steps for Assessing Retrofit Needs:
Preliminary Assessment: Conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the existing boiler system to determine its performance, efficiency, and emission levels, identifying existing problems and retrofit needs.
Data Collection and Analysis: Gather operational data of the boiler, including fuel consumption, thermal efficiency, emission levels, and operating costs, for detailed analysis.
Setting Goals: Based on the assessment results and the company's energy-saving and emission reduction targets, establish clear retrofit goals, such as improving thermal efficiency, reducing fuel consumption, and lowering emissions.
Planning the Retrofit Project:
Solution Design: Design a detailed retrofit plan based on the assessment results and retrofit goals, selecting appropriate retrofit technologies and equipment.
Budget and Schedule: Develop a project budget and implementation schedule to ensure the retrofit project is completed within the planned timeframe and budget.
Risk Assessment and Management: Identify potential risks and challenges and develop countermeasures to ensure the smooth progress of the retrofit project.
2. Installation Requirements
Key Steps in the Installation Process:
Preparation Work: Clear the installation site and ensure equipment and materials are ready. Train installation personnel to ensure they understand installation requirements and safety regulations.
Equipment Installation: Install the equipment according to the design plan, including the boiler body, burners, heat recovery systems, control systems, and auxiliary equipment.
System Integration: Ensure coordination and integration between subsystems, perform system commissioning and testing, and ensure normal system operation.
Coordination with Existing Operations:
Shutdown and Switching: Arrange shutdown and switching times reasonably during the installation process to minimize impact on production operations.
Communication and Coordination: Communicate closely with the production operation department to coordinate installation work and ensure a smooth installation process.
3. Maintenance Requirements
Maintenance Tasks After Retrofit:
Regular Inspections and Maintenance: Perform regular inspections and maintenance of the boiler system to ensure normal operation and stable performance of the equipment.
Cleaning and Repairs: Regularly clean the inside and outside of the boiler and repair key components, such as burners, heat recovery systems, and control systems, to prevent fouling and wear.
Importance of Regular Monitoring and Adjustments:
Performance Monitoring: Monitor the operating data of the system to detect and address issues in a timely manner, ensuring the boiler always operates in optimal condition.
Adjustment and Optimization: Make necessary adjustments and optimizations based on monitoring data to improve system operating efficiency and stability.
4. Lifecycle and Durability
Impact of Retrofit on Boiler Lifespan:
Extending Service Life: Improve boiler performance and efficiency through retrofitting, reducing failures and wear, and extending equipment service life.
Equipment Upgrades: Retrofitting may require replacing or upgrading some key components, further extending the boiler's service life.
Factors Affecting Long-term Durability:
Maintenance Quality: Regular maintenance and upkeep are crucial for long-term durability; lack of maintenance may lead to early equipment failure.
Operating Standards: Adhering to operating standards and safety procedures prevents damage to equipment from improper operation.
Environmental Conditions: The operating environment of the boiler, including temperature, humidity, and pollutants, also affects the long-term durability of the equipment.
FAQ
How much energy can be saved through retrofitting?
Energy-saving retrofits of gas-fired steam boilers can typically improve boiler thermal efficiency by 10-20%. The specific energy savings depend on the boiler's efficiency before the retrofit and the technologies applied. Common retrofit methods include installing high-efficiency burners, heat recovery systems, and optimizing control systems.
What is the typical payback period for boiler retrofits?
The payback period for boiler retrofits is usually 2-4 years, depending on the scale of the retrofit project, the initial investment, and the savings in fuel costs. Detailed return on investment (ROI) analysis can provide a more accurate prediction of the payback period.
Are there any government incentives for retrofitting boilers?
Many governments and regions offer various incentives to encourage enterprises to undertake energy-saving retrofits. These incentives include tax breaks, subsidies, low-interest loans, and technical support. Specific policies vary by location, so it is recommended to consult local energy management departments for detailed information.
How do I choose the right retrofit method for my boiler?
Choosing the appropriate retrofit method requires a comprehensive evaluation of the current condition of the boiler, retrofit goals, and budget. It is recommended to collaborate with a professional boiler retrofit company to develop the most suitable retrofit plan through data analysis and technical consultation.
What are the most common retrofit methods for gas-fired steam boilers?
Common retrofit methods include replacing high-efficiency burners, installing economizers and condensate recovery systems, upgrading automation control systems, adding insulation layers, and applying variable speed drives (VSD). These methods can significantly improve the boiler's thermal efficiency and operational stability.
Conclusion
Energy-saving retrofits of gas-fired steam boilers are crucial for improving energy efficiency, reducing operating costs, and minimizing environmental impact. By implementing advanced retrofit technologies, such as high-efficiency burners, heat recovery systems, and optimized control systems, enterprises can significantly reduce fuel consumption and emissions, enhancing the overall performance and stability of boilers. Additionally, energy-saving retrofits help enterprises meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations and achieve sustainable development goals.
Energy-saving retrofits are complex projects that require precise design tailored to specific operational environments and technical needs. To ensure the success of retrofit projects, enterprises are advised to consult with professional boiler retrofit experts for customized solutions. EPCB Boiler experts can provide comprehensive technical support and implementation guidance, helping enterprises optimize retrofit plans to achieve the best energy-saving results and return on investment.
If you are interested in boilers, feel free to contact EPCB Boiler. With our professional knowledge and extensive experience, we can help your enterprise achieve energy efficiency, environmental compliance, and sustainable development.
 Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler