Boilers power the industry, drive machinery, and sustain growth, but not all boilers are created equal. In today's industrial environment, choosing the right boiler technology can significantly impact efficiency, cost, and environmental footprint. Among the many options available, reciprocating grate boilers are prioritized for their unique combination of benefits to meet an increasingly diverse range of fuel sources and environmental considerations.
The energy mix in many regions is diverse, including natural gas, oil, coal, and other fuels. The ability of reciprocating grate boilers to burn a variety of fuels, such as coal, bituminous coal, and coal slurry, makes them ideally suited to energy market conditions. The efficient combustion characteristics of reciprocating grate boilers are particularly important given the shrinking supply of natural gas in many regions and the significant increase in the price of liquefied natural gas (LNG).
So why choose a reciprocating grate boiler? Next,EPCB Boiler will look at the definition of a reciprocating grate boiler, its energy efficiency, environmental performance, operational stability, fuel suitability, and cost to illustrate the benefits of choosing a reciprocating grate boiler for your industrial needs.
Definition of a Reciprocating Grate Boiler
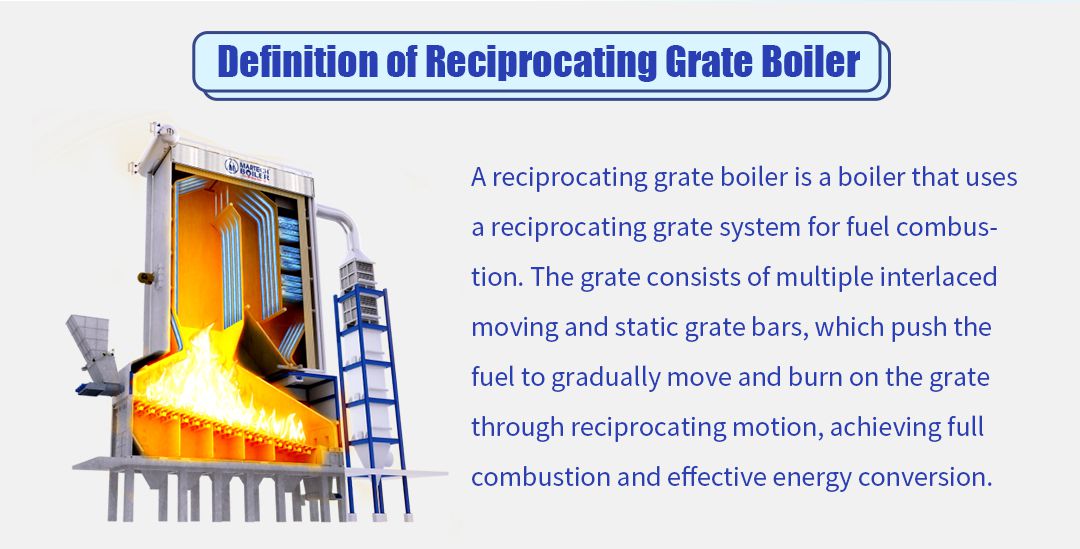
A reciprocating grate boiler is a boiler that uses a reciprocating grate system for fuel combustion. The grate consists of several interlocking movable and static grate bars, and the reciprocating movement promotes the gradual movement and combustion of fuel on the grate to achieve full combustion and effective energy conversion. In recent years, with the improvement of environmental protection requirements and the adjustment of energy structure, reciprocating grate boilers in the application of biomass fuel have been further developed.
Reciprocating grate technology originated in the early 20th century, with the development of industrialization and the need for efficient energy conversion, this technology has gradually developed. It was originally designed to address the limitations of traditional chain grate boilers in handling diverse fuels, especially those with high humidity or irregular shapes. With the development of material science and mechanical engineering, reciprocating grate boilers are gradually becoming widely used worldwide, especially in areas such as biomass and waste treatment.
Compared to chain grate boilers, reciprocating grate boilers are more flexible in terms of fuel handling. Chain grate boilers use a continuously running chain grate to transfer and burn fuel, and are suitable for burning fuels that are more uniform in particle size and drier. Reciprocating grate boilers, on the other hand, with their reciprocating grate bars, can handle fuels with higher moisture content and irregular shapes, such as wood chips, crop waste, and municipal solid waste. In addition, the reciprocating grate boiler allows for more uniform air distribution and fuel mixing during combustion, resulting in improved combustion efficiency and reduced emissions.
Principle of Operation
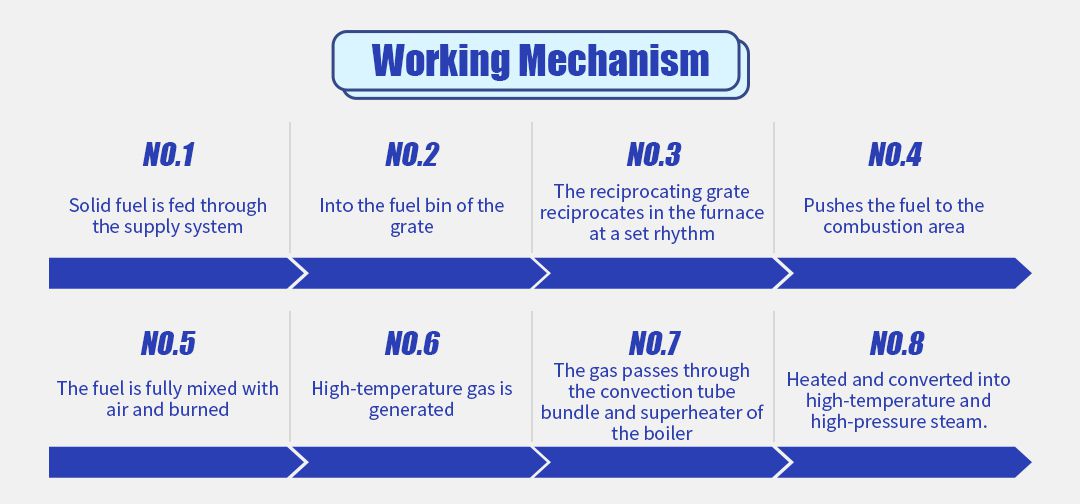
The principle of operation of a reciprocating grate boiler involves a series of successive steps. Firstly, solid fuel is added to the grate's fuel compartment via a supply system. Subsequently, the fuel is pushed into the combustion zone by the reciprocating grate, which moves back and forth in the furnace chamber according to a set rhythm. In the combustion zone, the fuel is mixed with air and combusted to produce high-temperature gases. These high-temperature gases are then passed through the boiler's convection tube bundles and superheaters, where they are heated and converted into high-temperature, high-pressure steam.
Reciprocating grate boiler through a series of staggered arrangements of dynamic and static grate bar reciprocating motion to convey and burn the fuel, to achieve sectional combustion, and to achieve the purpose of full combustion. The reciprocating movement of the reciprocating grate is the key to the combustion process. When the grate reciprocates downward, the solid fuel is pushed into the combustion zone. This movement contributes to improved ignition conditions due to the relative motion between the grate and the fuel.
The fuel is added to the fuel compartment of the grate via a supply system and is then pushed into the combustion zone by the reciprocating movement of the grate. The fuel moves slowly from front to back along the inclined grate surface and passes through the stages of preheating and drying, volatile analysis ignition, coke combustion, and ash burnout. Under the reciprocating feeding action of the movable grate, the fuel is fully mixed with air and burned.
Advantages of Reciprocating Grate Boiler
In the industrial steam boiler system, the reciprocating grate boiler with its unique design and excellent performance, has become the first choice for many industries. Designed to improve combustion efficiency, reduce fuel consumption, and optimize operational control, the reciprocating grate boiler provides a reliable and cost-effective solution. The key benefits of reciprocating grate boilers are explored in more detail below to help organizations make informed decisions when selecting an industrial boiler system.
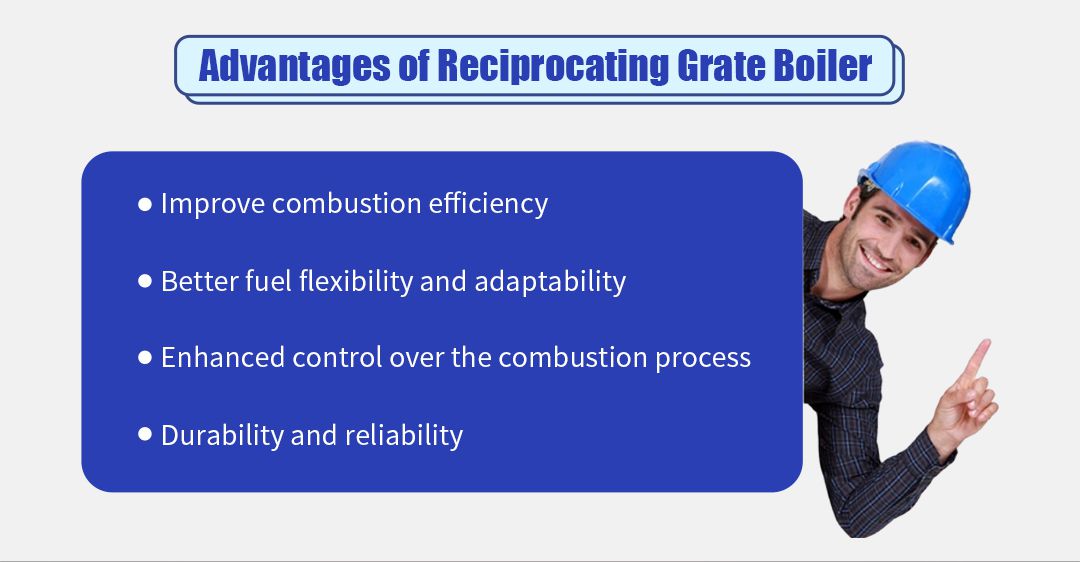
Firstly, it achieves an even supply of fuel through the reciprocating grate. The reciprocating motion causes the fuel to turn and move forward, ensuring full contact between the fuel and the air, and the fuel goes through different stages of drying, catching fire, and burning out on the grate, with the environmental conditions (such as temperature and oxygen supply) optimized for each stage, which effectively improves the combustion efficiency and reduces the energy consumption.
Secondly, the reciprocating grate boiler has good flexibility and adaptability to fuels and can handle many types of fuels, including wood chips, sawdust, crop wastes, municipal solid wastes, etc. It is especially suitable for fuels with high humidity or irregular shapes, which provides users with more space for choice. The combustion process of different types and characteristics of fuels on the grate can be optimized by reciprocating grate movement, air supply, and other parameters, and the best combustion results can also be achieved.
Furthermore, reciprocating grate boilers are also characterized by high durability and reliability. Reciprocating grate boilers are designed with a sturdy structure, and the grate is made of high-temperature and abrasion-resistant materials with a long service life. The mechanical structure of the reciprocating grate system is simple and reliable, with fewer moving parts and a low failure rate, which reduces the frequency of maintenance and replacement of parts. At the same time, its load resistance is strong and can withstand large load changes, to ensure the continuity and stability of production.
Finally, the reciprocating grate boiler also performs well in smoke elimination, which contributes to environmental protection. Reciprocating grate boiler combustion efficiency, combustion produces less smoke and harmful gases. At the same time, reciprocating grate boilers are usually equipped with flue gas treatment equipment, such as dust collectors, desulphurization devices, etc., which can effectively remove soot, sulfur dioxide, and other hazardous substances, and further reduce the pollution of the environment. In addition, the high combustion efficiency of reciprocating grate boilers can effectively utilize the heat energy of the fuel, reduce the consumption of fuel, and lower the emission of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, which is of positive significance in reducing energy consumption and mitigating the greenhouse effect.
Efficiency and Performance
In terms of efficiency, reciprocating grate boilers exhibit commendable performance indicators. They outperform their counterparts in terms of fuel economy and energy output. Case studies and performance vividly illustrate why these boilers are a model of operational efficiency.
Reciprocating grate boilers typically have combustion efficiencies between 80 and 90 percent, depending on fuel type and operating conditions. The reciprocating motion of the reciprocating grate ensures that the fuel is well mixed with the air for complete combustion. This means that more of the fuel energy can be efficiently converted into heat.
Chain grate boilers usually require drier and more homogeneous fuels, which require a high degree of fuel pre-treatment. Due to the faster movement of the fuel on the chain grate, the combustion time is shorter and the combustion is not sufficient, the combustion efficiency and thermal efficiency are relatively low, usually between 70% and 80%.
Fluidized bed boilers can burn a variety of fuels, including inferior fuels, with high fuel adaptability. As the fuel is fully mixed and combusted in the fluidized bed, the combustion efficiency and thermal efficiency are higher, usually above 85%, but the system is complex and the maintenance requirements are high.
Case One
A biomass power plant replaced the old chain grate boiler with a new reciprocating grate boiler. The combustion efficiency was increased from 75% to 88%, saving about 20% of the annual fuel cost and increasing the energy output by 15%. Comparative data on energy consumption and capacity before and after the boiler modification showed that the new boiler operated stably and fuel consumption was significantly reduced.
Case Two
An industrial enterprise used a reciprocating grate boiler to replace a traditional chain grate boiler for heat supply in the production process. The overall thermal efficiency was increased by 12%, operating costs were reduced by 10%, and the number of maintenance visits was reduced by 30%. The company's operation report shows that the new boiler not only improves production efficiency but also reduces operation and maintenance costs.
As you can see, higher combustion efficiency means that fuel is utilized more fully, which reduces fuel consumption and directly reduces fuel costs. Reciprocating grate boilers are highly adaptable to fuel types, allowing the use of lower-cost biomass fuels or wastes for further cost savings.
Higher thermal efficiency means that more heat energy is produced per unit of fuel, boosting the boiler's energy output and thus improving overall capacity and efficiency. On top of that, the design of reciprocating grate boilers reduces fuel build-up and clogging problems, lowering maintenance frequency and costs. At the same time, a highly efficient boiler plant also means lower operating costs and a longer service life, which improves overall operational efficiency.
Environmental Advantages

In an era where regulatory compliance and sustainability are primary considerations, the environmental benefits of reciprocating grate boilers are critical. Reductions in pollutant and greenhouse gas emissions are a testament to the cleaner combustion process provided by reciprocating grate boilers.
The use of reciprocating grate boilers offers significant advantages in terms of environmental benefits in terms of reduced pollutant and greenhouse gas emissions, better handling of various biomass fuels for more sustainable operations, and strict compliance with environmental regulations and standards. Firstly, by precisely controlling the combustion process, reciprocating grate boilers can significantly reduce emissions of pollutants such as soot, sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and other pollutants, reducing pollution of the atmosphere.
Secondly, when using biomass fuels, these boilers can achieve lower greenhouse gas emissions because the carbon dioxide (CO2) released during the combustion of biomass fuels is comparable to the CO2 absorbed during their growth, making them carbon neutral. In addition, the fuel adaptability and flexibility of reciprocating grate boilers allow them to handle a wide range of biomass fuels, thus enabling waste utilization and resource recycling for sustainable development.
Cost Considerations

Examining the cost elements associated with reciprocating grate boilers reveals the relationship between initial investment and long-term savings. While the upfront costs may seem significant, substantial operation and maintenance savings mitigate these costs over time.
The cost of the initial investment includes advanced technology and design features, as well as additional equipment or systems that may be required to support its operation. However, the high efficiency and low fuel consumption characteristics of reciprocating grate boilers enable significant energy savings and cost reductions to be realized during operation. In the long term, these advantages will translate into greater cost-effectiveness, as users will enjoy lower fuel costs, electricity costs, and possibly maintenance costs.
In addition, the high level of automation in reciprocating grate boilers reduces reliance on labor, further reducing labor costs. Taking into account the initial investment, maintenance costs, and operating costs, reciprocating grate boilers demonstrate significant economic advantages. Therefore, the reciprocating grate boiler is a worthwhile option in terms of cost-effectiveness.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Reciprocating grate boilers have demonstrated excellent performance and wide applicability in several industries. In the power generation industry, they are particularly suitable for biomass power generation and waste-to-energy incineration, where waste is converted into electricity through the efficient combustion of biomass fuels or waste, achieving a win-win situation in terms of environmental protection and economic benefits. In the manufacturing sector, whether in metalworking, chemicals, or building materials, reciprocating grate boilers play a key role in processes such as heating, drying, and sintering, improving product quality and productivity. Although there are fewer examples of direct use in agro-processing, their potential value in the use of biomass energy for the treatment of agricultural waste provides the possibility of resource utilization of agricultural waste. In terms of environmental protection and resource utilization, reciprocating grate boilers demonstrate significant environmental benefits by reducing dependence on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. In addition, reciprocating grate boilers have demonstrated outstanding performance in catalyst activation processes in the chemical industry and the high-temperature drying and sintering of stone, ceramics, and other materials in the building materials industry. Through continuous design optimization and technical improvement, reciprocating grate boilers will continue to play an important role in the field of energy use and environmental protection.
FAQ
What are the main advantages of reciprocating grate boilers over other boilers?
Reciprocating grate boilers are known for their efficient combustion and fuel flexibility. They are designed to achieve multiple combustion of fuel through the reciprocating motion of the reciprocating grate, which improves fuel utilization and overall thermal efficiency. This efficient combustion allows the fuel to burn more fully, significantly reducing energy losses. At the same time, the reciprocating grate boiler can also burn a variety of fuels, including power coal, bituminous coal, coal slurry, wood and biomass fuels, etc. It is particularly suitable for handling uneven and irregularly shaped fuels, and this flexibility makes it adaptable to different fuel supply situations, providing more choices for the user.
How does the maintenance of a reciprocating grate boiler compare to other boilers?
Reciprocating grate boiler requirements in terms of maintenance mainly focuses on regular inspection of the wear and tear of key components such as grate blades, chains, bearings, etc., and the necessary lubrication and maintenance to ensure that these components are operating in the best condition. In addition, timely cleaning of ash and slag accumulation in the combustion chamber, flue, etc. is carried out to maintain combustion efficiency and safety. Proper fuel management is also an important part of maintenance to ensure a stable supply of fuel and to avoid damage to the boiler caused by the use of poor quality fuel. Because reciprocating grate boilers are designed with long-term operation in mind, using high-temperature and abrasion-resistant materials for key components, as well as a simple structure with few mechanical parts, they have a relatively low failure rate and demonstrate high long-term reliability.
Are reciprocating grate boilers suitable for all types of biomass fuels?
The reciprocating grate boiler is not suitable for all types of biomass fuels, although it offers good fuel flexibility. However, it has shown good adaptability in handling a wide range of biomass fuels, especially biomass pellets, straw, and wood chips. These biomass fuels have the advantages of high combustion efficiency, high energy density, and harmless combustion products, which make them ideal for use in reciprocating grate boilers. When selecting fuels, comprehensive consideration needs to be given to the combustion characteristics of the fuel, its physical properties, and the degree of compatibility with the boiler design to ensure an efficient and safe combustion process. Therefore, reciprocating grate boilers are suitable for the use of various types of biomass fuels such as biomass pellets, straws, and wood chips.
 Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler